CYBER SECURITY CONSULTING SERVICE AWARDS AND RECOGNITIONS
CyberSecOp's comprehensive managed security services, cyber security consulting, professional services, and data protection technology are recognized as industry-leading threat detection and response solutions by major analyst firms, key media outlets, and others.
Benefits of Mobile device management (MDM)
Mobile device management (MDM) is a type of security software used by an IT department to monitor, manage and secure employees' mobile devices that are deployed across multiple mobile service providers and across multiple mobile operating systems being used in the organization. Mobile device management (MDM) capabilities give you the fundamental visibility and IT controls needed to secure, manage, and monitor any corporate or employee owned mobile device or laptops that accesses business critical data.
Mobile device management (MDM) solution provides immediate, on-device threat protection, protecting against device, app and network threats even when the device is offline.d:
Detect the attack immediately
Notify the device user through mobile clients and enterprise admin through centralized console
Take preventive actions to protect company data through custom compliance actions
Administrators can use our capabilities to find all the devices that have the vulnerable versions of WhatsApp on them and assign compliance actions to only those devices, while not affecting the productivity of users running updated version of the compromised app.
Benefits of Mobile device management (MDM)
More control and security
An effective MDM system guarantees the protection of company data, e-mails, and confidential documents. If a device is lost or stolen, the administrator can easily lock, disconnect, or lock the mobile device. SIM cards can also be blocked for employees’ mobile devices and if somebody tries to transfer the SIM to another device they will need a PUK code.
MDM offers better control over their devices. For example, a company’s sales employee will not have to register and configure all devices used by their sales agents. Instead, you can configure the device and use the security software automatically. Certain tools and applications can also be sent to agent devices. If you want the app to be configured at start-up or if you want an automatic application or replacement updates throughout the enterprise, you can easily do it manually without having to call the device.
Powerful and Highly Efficient Management
Practically, mobile devices can distract employees. If organizations want to limit or prohibit the use of certain apps on their devices and avoid unnecessary data costs, IT managers can block YouTube, Facebook, or other social media apps. Take, for example, the company’s rescue services. As drivers need to focus on the road, some companies use MDM to prevent them from using other apps than the transport app and Waze or Google Maps while driving. This not only ensures operational efficiency, but also security
Increased flexibility
Working from anywhere with a mobile device gives access to relevant files anytime, anywhere and in any situation. Some tools gives you that luxury, for example, the vendors of the company do not need to download the resources separately from different portals. The centralized MDM system enables more efficient distribution of business documents, such as training forms and learning materials, accessible only to authorized individuals.
Find the right MDM solution
As the businesses focus on productivity, efficiency, and security, and with more and more companies choosing BYOD (Bring your own device), MDM is ready to respond to feature requests that help them take control of the device while providing their employees with freedom, security, and productivity.
Ransomware - SMEs Faces Greatest Risk - Attacks Grown 235%
Enterprises, beware. Threat actors are continuing to eye businesses for high returns on investment in Q1 2019, breaching infrastructure, exfiltrating or holding data hostage, and abusing weak credentials for continued, targeted monitoring. From a steadfast increase of pervasive Trojans, such as Emotet, to a resurgence of ransomware lodged against corporate targets, cybercriminals are going after organizations with a vengeance.
Ransomware attacks on business targets have seen a substantial increase in the first quarter of 2019, up by 195 percent since the fourth quarter of 2018, according to a recent Malwarebytes report.
Malwarebytes researchers analyzed the combined statistics and intel collected from its intelligence, research, and data science teams between January 1 and March 31, 2019. They also leveraged telemetry from both consumer and business products on PC, Mac, and mobile devices.
Overall, they found that business detection of ransomware attacks increased by more than 500 percent from the same time frame in 2018 with 336,634 detections.
SMEs face the greatest risk from attacks as overall business detections have grown 235%
“Zero day attacks are on the rise and estimated to be a daily occurrence by 2021. This is largely down to digitisation within organisations and there’s more pressure on developers to deliver software faster – leaving systems vulnerable. This problem is exacerbated by hackers becoming more sophisticated, enabling them to bypass defences more easily.
“IT teams often prioritise stopping a breach occurring at all, but in today’s cyber climate a successful breach is inevitable. The most important aspect of cyber security is that businesses prepare for the worst and have effective data recovery and backup systems in place. Zero day recovery makes sure critical systems are down for as little time as possible. It’s often true that real damage from these breaches doesn’t come from the attack itself, but the resultant downtime after a breach – the time taken to become fully operational dictates the financial and operational fallout on a business.”
Key takeaways
cryptomining seems to have gone the way of the dodo. Detections of consumer-focused Bitcoin miners have dropped significantly over the last year and even from last quarter, while business-focused miners have increased from the previous quarter, especially in the APAC region.
Adware in Macs and mobile devices was problematic.
While all Mac malware saw a more than 60 percent increase from Q4 2018 to Q1 2019, adware was particularly pervasive, clocking in at over 200 percent from the previous quarter. Mobile adware detections also trended upward, as supply chain attacks delivered malware pre-installed on mobile devices. However, overall adware detections were fewer in Q1 2019 than they were during the same time period last year.
Exploit authors developed some attention-grabbing techniques. A new Flash Player zero-day was discovered in Q1 and quickly implemented into popular exploit kits, including Underminer and Fallout EK, as well as a new exploit kit called Spelevor. In addition, a Chrome zeroday required users to take action, fully shutting down and restarting their browser in order to patch the vulnerability. Finally, the popular software WinRAR was being used to deliver payloads to users.
As attacks against businesses ramped up, user trust in businesses to protect their data reached a new low.
In a survey conducted by Malwarebytes in Q1 2019 of nearly 4,000 respondents, users expressed deep concerns about abuse, misuse, and theft of PII, especially from social media and search engine companies. In a new section of our Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques report, we examine how cybercriminals found success by exploiting infrastructure weaknesses, gaps in policy and regulation, and even corporate negligence to not only walk away with valuable data, but establish persistence within the network.
Businesses are still the prime target. Overall detections of threats to businesses have steadily risen, while consumer threats have dropped off. Business detections increased by about 7 percent from the previous quarter, while consumer detections declined by nearly 40 percent, resulting in an overall dip in malware volume of 35 percent quarter over quarter. Compared to Q1 2018, business detections have skyrocketed 235 percent, with consumer detections dropping 24 percent year over year. This reinforces the observed trend of cybercriminals focusing more on business targets today.
Emotet shows no signs of stopping. Emotet, the most fearsome and dangerous threat to businesses today, has made a total shift away from consumers, reinforcing the intent of its creators to focus on enterprise targets, except for a few outlier spikes. Detections of Trojans (Emotet’s parent category) on business endpoints increased more than 200 percent from the previous quarter, and almost 650 percent from the same time last year.
Ransomware is back to business.
Ransomware has made a tremendous comeback against business targets in Q1 2019, with an increase of 195 percent in detections from Q4 2018 to Q1 2019. In comparison to the same time last year, business detections of ransomware have seen an uptick of over 500 percent, thanks in large part to a massive attack by the Troldesh ransomware against US organizations in early Q1.
Consumer detections of ransomware died down. Meanwhile, ransomware consumer detections have continued to drop, despite activity by families such as GandCrab, which primarily targeted consumers over the last quarter as it switched to a ransomware-asa-service and began brute-forcing RDP to infiltrate systems. Consumer detections of ransomware decreased by 10 percent quarter over quarter, and by 33 percent year over year.
Decrease Potential Data Breach, with Simple Security Control
Some senior management folks might find this strange, but you can significantly make your organization harder to breach. In fact, just a handful of defenses can do more to lower your cybersecurity risk than anything else. These include fighting social engineering and phishing better, patching the most likely to be attacked software far better, and requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all logons.
Zero-day and information system protection
Because zero-day flaws usually refer to software that is widely in use, it’s generally considered good form if one experiences such an attack to share any available details with the rest of the world about how the attack appears to work — in much the same way you might hope a sick patient suffering from some unknown, highly infectious disease might nonetheless choose to help doctors diagnose how the infection could have been caught and spread. patch management is critical in protecting information technology systems.
Ransomware Breach and Criminals
The typical use case for ransomware is a shotgun approach type distribution campaign of dropping ransomware on people's machines, and then you charge them for getting their data or services back,” says Jeffery Walker, CISO at CyberSecOp. “Another use case is for covering tracks. These tools have the façade of ransomware: They would encrypt data, they would post a ransom note, and they would ask for money. They will even give you details on how to pay, but they're used to remove things from the endpoint while throwing off defenders into believing that the reason why that data was lost was because of a random hit by ransomware, but in some cases this is a cover up of a more bigger breach”
Vulnerabilities and Exploits
These are all vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals bent on stealing personally identifiable information and protected health information – activity that could also play havoc disrupting healthcare delivery processes.
The study, based on network traffic data monitored by CyberSecOp over a six-month period, found the most prevalent method attackers use to hide command-and-control communications in healthcare networks was hidden HTTPS tunnels.
CyberSecOp compliance solutions deliver cost-effective data protection, data discovery, data classification and data loss prevention for data privacy and compliance.
What is Computer Security, Network Security and Cyber Security?
They have different responsibilities, but both plays apart in securing your organization
Network security is concerned about maintaining peace and calm within the walls of the castle. It focuses on maintaining the fortifications, of course, but its primary purpose is to guard against problems from within. A person concerned with network security will be focusing on protecting a company's internal information by monitoring employee and network behavior in several ways. They are the shire reeve responsible for keeping peace in the land.
IDs and passwords - making certain they are effective and updated frequently
Firewalls - keeping outside threats at bay
Internet access - monitoring the sites employees visit on the company's computers
Encryption - making certain that company information is useless to anyone outside the company
Backups - scheduling regular backups of company information in case of a hardware malfunction or successful outside threat
Scans - conducting regular virus and malware scans to detect any outside infection
Cyber security is much more concerned with threats from outside the castle. Where network security is worried about what is going on within the castle walls, cyber security is watching who is trying to pass through the gate or breach the parapets. The two areas have a lot of overlap, but their areas of concern are quite different. The cyber security specialist is the crusading knight defending the kingdom. Cyber security focuses on the barbarians at the gate and how the castle connects to the world around it.
Network protection - detecting and protecting against outside attempts to get into the network
Up-to-date information - staying informed on how attackers and hackers are improving their efforts
Intelligence - identifying the sources of outside attacks and protecting against them
Applications - monitoring the use of applications to avoid unintended breaches from within
What is Computer Security/Network Security
Computer security, or information technology security is the protection of computer systems from theft or damage to their hardware, software or electronic data, as well as from disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. information technology consulting as a field of activity focuses on advising organizations on how best to use information technology in achieving their business objectives, computer security is. usually managed by a network engineer or a network consultant.
What is an Network Consultant
a network consultant might be a network architect, a system administrator, a security specialist, or a number of different things. These consultants are responsible for designing, setting up, maintaining, and securing computer networks. Computer network architects gather extensive knowledge of an organization’s business plan in order to design and build data communication networks that can help the organization achieve its goals. This data communication network includes local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and intranets.
Network Engineer Responsibilities: Maintaining and administering computer networks and related computing environments including systems software, applications software, hardware, and configurations. ... Protecting data, software, and hardware by coordinating, planning and implementing network security measures
What is Cyber Security
Cybersecurity is the protection of internet-connected systems, including hardware, software and data, from cyberattacks. In a computing context, security comprises cybersecurity and physical security -- both are used by enterprises to protect against unauthorized access to data centers and other computerized systems.
What is a cyber security consultant
A cyber security consultant performs a variety of roles within the cyber security field. They play both the attacker and the defender in computer systems, networks, and software programs. Seeing what weaknesses there are and figuring out how to strengthen systems to prevent hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities.
A security consultant is a catch-all cybersecurity expert. They assess cybersecurity risks, problems and solutions for different organizations and guide them in protecting and securing their physical capital and data, Earn a mid-level role as a security administrator, analyst, engineer or auditor.
Cyber Security Engineer Responsibilities: Planning, implementing, managing, monitoring and upgrading security measures for the protection of the organizations data, systems and networks. Troubleshooting security and network problems. Responding to all system and/or network security breaches.
Ransomware Attack: Threats, and Countermeasures
When you combine cryptography with malware, you get a very dangerous mix of problems. This is a type of computer virus that goes by another name, “ransomware”. This type of virus is part of a field of study called “cryptovirology”. Through the use of techniques called phishing, a threat actor sends the ransomware file to an unknowing victim. If the file is opened it will execute the virus payload, which is malicious code. The ransomware runs the code that encrypts user data on the infected computer or host. The data are user files like documents, spreadsheets, photos, multimedia files and even confidential records. The ransomware targets your personal computer files and applies an encryption algorithm like RSA which makes the file inaccessible. The only way to access them is if the user pays a ransom to the threat actor by following instructions which appear encoded into the encrypted files. Thus it is called ransomware, because a form of payment is demanded in order to fix the problem.
Once they have all publicly available email addresses, the fun starts. The more of your email addresses that are floating out there, the bigger your attack footprint is, and the higher the risk is. It’s often a surprise how many addresses are actually out there. Now they can send all employees an email supposedly coming from Accounting, Human Resources, the CEO or perhaps the mail room, and social engineer your users to click on a link. almost 90 percent of attack are done via the internet, based on the new software model, and yes the bad guys are also moving to the cloud. Software is shifting away from locally-installed apps to Software as a Service web applications that run in the cloud. Criminals are cashing in on this trend, which has led to the creation of Ransomware as a Service (RaaS), a growing threat to business.
RaaS refers to various online malware exploits that bad actors can use to attack the IT assets of businesses and individuals. These attack programs are created by criminal entrepreneurs who sell their services to other criminals. The people who buy these programs then extort or blackmail their victims by holding computer systems to ransom.
How does Ransomware spread?
Ransomware is typically spread through phishing emails that contain malicious attachments. These emails appear to come from a legitimate source and give a compelling reason that the document is important. Malicious attachments are often PDF, ZIP, DOC, XLS, PPT files that appear as invoices, legitimate business documents, or other work-related files. In some cases, Ransonware may end up on your computer by visiting infected web sites. To avoid malicious drive-by downloads, ensure that antivirus and all installed software is up-to-date.
How to Mitigate the Risk of Ransomware Infections
These recommendations are not comprehensive but provide general best practices.
Securing Networks and Systems
Have an incident response plan that includes what to do during a ransomware event.
Backups are critical. Use a backup system that allows multiple iterations of the backups to be saved, in case a copy of the backups includes encrypted or infected files. Routinely test backups for data integrity and to ensure it is operational.
Use antivirus and anti-spam solutions. Enable regular system and network scans with antivirus programs enabled to automatically update signatures. Implement an anti-spam solution to stop phishing emails from reaching the network. Consider adding a warning banner to all emails from external sources that reminds users of the dangers of clicking on links and opening attachments.
Disable macros scripts. Consider using Office Viewer software to open Microsoft Office files transmitted via e-mail instead of full office suite applications.
Keep all systems patched, including all hardware, including mobile devices, operating systems, software, and applications, including cloud locations and content management systems (CMS), patched and up-to-date. Use a centralized patch management system if possible. Implement application white-listing and software restriction policies (SRP) to prevent the execution of programs in common ransomware locations, such as temporary folders.
Restrict Internet access. Use a proxy server for Internet access and consider ad-blocking software. Restrict access to common ransomware entry points, such as personal email accounts and social networking websites.
Apply the principles of least privilege and network segmentation. Categorize and separate data based on organizational value and where possible, implement virtual environments and the physical and logical separation of networks and data. Apply the principle of least privilege.
Vet and monitor third parties that have remote access to the organization’s network and/or your connections to third parties, to ensure they are diligent with cybersecurity best practices.
Participate in cybersecurity information sharing programs and organizations, such as MS-ISAC and InfraGard.
Securing the End User
Provide social engineering and phishing training to employees. Urge them not to open suspicious emails, not to click on links or open attachments contained in such emails, and to be cautious before visiting unknown websites.
Remind users to close their browser when not in use.
Have a reporting plan that ensures staff knows where and how to report suspicious activity.
Responding to a Compromise/Attack
Immediately disconnect the infected system from the network to prevent infection propagation.
Call CyberSecOp.com Ransomware Response Team: They provide remediation and bitcoin payment services.
Determine the affected data as some sensitive data, such as electronic protected health information (ePHI) may require additional reporting and/or mitigation measures.
Determine if a decryptor is available. Online resources such as No More Ransom! can help.
Restore files from regularly maintained backups.
Report the infection. It is highly recommended that SLTT government agencies report ransomware incidents to MS-ISAC. Other sectors and home users may report to infections to local Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) field offices or to the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
Ransomware Checker & Removal Tools
Why You Need a Cybersecurity Management Program
Many organization’s cybersecurity teams (or information security teams as they used to be known) continue to struggle to communicate cybersecurity issues to senior leadership. Likewise, senior management also struggles to effectively articulate cybersecurity strategy to technical cybersecurity personnel. It is as though two parts of the same organization speak foreign languages to one another, and each party has a very limited, or no, knowledge of the other party’s language. However, it does not have to be like this.
Why so many organizations struggle with Cyber Security
Failure to communicate issues is most often revealed in grassroots cybersecurity initiatives that have evolved into corporate cybersecurity programs. Typically, this resulted from an enterprise in startup mode implementing solutions to address specific technical challenges. Unfortunately, many organizations continue to employ a similar approach to secure much larger and more complex environments against threats that outmatch the capabilities of their original solutions. No longer simply a technical solution, cybersecurity management has become a business function in today’s industry. As a business function, a greater level of integration with other business units requires a greater level of transparency and performance reporting. The evolution of grassroots cybersecurity programs rarely results in the kind of mature cybersecurity solutions that are aligned with, and address business needs. And why should they? The initial programs were designed to solve technical challenges, such as preventing virus outbreak or infection, stopping cyber attackers from compromising or stealing valuable information. Such initial cybersecurity efforts were neither designed as business functions nor defined in business terms.
CyberSecOp Comprehensive Security Program - Going beyond compliance
Cyber Security Program Key Success Factors
The following key success factors are common to many successful cybersecurity programs. The programs:
Support and drive strong governance attitudes and actions
Are designed, developed, and implemented in a similar way to other business functions
Adopt a standard framework approach, usable for an extended period of many years with little or no changes to that framework
Are measureable in terms of their effectiveness
Organizations and executives that drive successful cybersecurity programs do so in the same manner as other successful business initiatives. Executives succeed at this not because of industry pressure, but because each aims to improve their organization. Having identified the opportunity, executives evaluate whether the initiative poses additional risks to their organizations and decide whether to accept this additional risk or not. After accepting such risk, executive sponsors continue to evaluate initiatives toward implementation. Even when initiatives are operational, executives still employ strong governance methods, including internal audit teams, to manage and monitor the effectiveness and efficiency of these initiatives. This business approach has become institutionalized across most enterprise units with the exception of IT and cybersecurity. Key stakeholders in IT and cybersecurity often claim that cybersecurity management programs are too technical, only internal facing, or too complex, to properly develop and implement using this approach.
The truth is if these same IT and cybersecurity groups adopted a common framework and designed their cybersecurity management programs based on said framework, cybersecurity management would truly become just a standard business function in their enterprises. Unfortunately, the cybersecurity world does not agree on a standard cybersecurity framework across all countries, industries, and states. Analysis of the commonalities and differences between these standard frameworks show that it is possible to create a universal cybersecurity management framework to address all countries, industries, and states. Such a framework is not firmly associated with any particular cybersecurity standard and can be adapted during implementation to address any specific security standard that organizations using it wishes to follow. This paper introduces a cybersecurity management framework where it is apparent that a successful approach is not too technical, addresses both internal and external concerns, and is not overly complex to implement, operationalize, and manage over the long term.
CyberSecOp Cyber Security Management - Aligning businesses with security
Cybersecurity Management Framework
The design of the CyberSecOP cybersecurity management framework (CMF) assumes cybersecurity management is a business function.
The framework, as a business function, is comprised of three discrete pillars with each subsequent layer unfolding increasing levels of specificity as follows:
The Executive Management (Strategy) Pillar directs Governance and Planning initiatives that drive the framework forward to operation.
The Executive Management Pillar requires people to identify why cybersecurity is needed, consider the business issues, and then define, document, and publish the direction the required cybersecurity program will adopt.
The Operations Pillar that defines what the cybersecurity program must address to comply with the requirements specified in the strategy, what supporting functions are needed, and what level of reporting/ governance monitoring should be provided. These needs are supported through the security intelligence, IT and Cybersecurity Assurance and IT Risk Management operations sub-pillars.
The Operations Pillar requires definitions of documented operational standards, processes, procedures, and other collateral that specify what operators should do and how they should do it.
The Tactical (Technology) Pillar defines how required cybersecurity controls mandated in the Operations and Executive Management pillars will be applied to the systems, networks and applications used by the organization and how evidence will be provided to management that the security controls implemented actually address the specific requirements and that they perform their job as expected.
The security controls in the Tactical pillar, whether requiring technology or not, are responsible for securing all aspects of an enterprise computing environment, continuously monitoring the environment for security events, collecting and analyzing captured events, and reporting defined security metrics, some of which are provided to the SLT.
Addressing Cybersecurity Challenges
Although addressing cybersecurity challenges with just three pillars is perfectly possible, adopting and using it in that way is difficult and potentially open to error or misinterpretation. To minimize these issues, these macro-level pillars must be divided into more manageable chunks. The CyberSecOp LocPar subdivides its three macro pillars into seven discrete focus areas:
Executive Management: Key decisions and accountability required to drive the program
IT Risk Management: Reducing risk exposure to the organization to a level acceptable to the SLT and Board of Directors.
Cybersecurity Intelligence: Required to provide the cybersecurity and IT teams with appropriate information to achieve and surpass IT Risk Management goals.
IT and Cybersecurity Assurance: Required to provide evidence to management and especially the SLT that their investments in cybersecurity are delivering the benefits they expected.
Secure Network: Required to support secure, on demand access to information to authorized personnel no matter where it is located within, or external to, the organization.
Secure Systems: Required to provide controlled access to applications, data and devices according to the identity of the requesting party. This focus area also includes how data is protected, whether at rest, or in transit.
Secure Applications: Required to control access to data and other networks, systems and applications according to the identity of the requesting party. For internally developed applications, requirements extend to how the application was designed, developed and managed throughout the whole development lifecycle.
Summary
Development, implementation, and maintenance of a cybersecurity management program for an organization is no small undertaking. However, the overall value that organizations achieve through development and implementation of such programs includes reduced instances of successful cyber attacks. Moreover, a cybersecurity management program provides organizations with a means to reduce a successful attack’s impact on the bottom line due to its programmatic predefined approach for identifying and responding to cybersecurity incidents. Read more about cybersecurity management programs and CyberSecOp Cybersecurity Services at https://www.cybersecop.com/
Addressing Cyber Threats and Enabling Security in your Enterprise
Cybersecurity threats from hacktivists, criminals, and hostile nation states are enough to keep government officials, businesses, and consumers up at night. These attacks are growing in sophistication and frequency and pose serious threats to our national and economic security.
Everyone impacted by these vicious and dangerous acts must work together to help prevent, protect against, and effectively respond to them.
What are the biggest cyber threats CISOs are worried about in 2019? In today's age of breaches, staying ahead of cyber threats is becoming more critical than ever. Dive into how organizations are addressing the threat of cyber attacks, how they are measuring risk, and what they are doing about improving security from some of the top experts in the field.
Ransomware is still a large risk, affecting a large number of businesses
Data Loss and Data Breach based on information available on dark web, proves that organization can’t protect customers data.
Small business with no security program are at risk more than large organization.
All industry need to have some type of cyber regulations based on secure standards such as NIST or ISO.
What can business do, to enable a stronger security posture in their enterprise
Businesses adopt standalone cyber insurance policies as boards and executives wake up to cyber liability. As boards and executives experience and witness the impact of cyber attacks, including reduced earnings, operational disruption, and claims brought against directors and officers, businesses will turn to tailored enterprise cyber insurance policies, rather than relying on “silent” components in other policies. Adoption will spread beyond traditional buyers of cyber insurance, such as retail, financial, and healthcare sectors, to others vulnerable to cyber-related business disruption, including manufacturing, transportation, utility, and oil and gas.
As the physical and cyber worlds collide, chief risk officers take center stage to manage cyber as an enterprise risk. As sophisticated cyber attacks generate real-world consequences that impact business operations at increasing scale, C-suites will wake up to the enterprise nature of cyber risk. In 2018, expect CROs to have a seat at the cyber table, working closely with chief information security officers (CISOs) to help organizations understand the holistic impact of cyber risk on the business.
Regulatory spotlight widens and becomes more complex, provoking calls for harmonization. EU holds global companies to account over General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) violation; big data aggregators come under scrutiny in the U.S. In 2018, regulators at the international, national and local levels will more strictly enforce existing cybersecurity regulations and introduce new regulations. Expect to see EU regulators holding major U.S. and global companies to account for GDPR violations. Across the Atlantic, big data organizations (aggregators and resellers) will come under scrutiny on how they are collecting, using, and securing data. Industry organizations will push back on regulators, calling for alignment of cyber regulations.
Criminals look to attack businesses embracing the Internet of Things, in particular targeting small to mid-sized businesses providing services to global organizations. In 2018, global organizations will need to consider the increased complexities when it comes to how businesses are using the IoT in relation to third-party risk management. The report predicts large companies will be brought down by an attack on a small vendor or contractor that targets the IoT, using it as a way into their network. This will serve as a wake-up call for large organizations to update their third-party risk management, and for small and mid-sized businesses to implement better security measures or risk losing business.
As passwords continue to be hacked, and attackers circumvent physical biometrics, multi-factor authentication becomes more important than ever before. Beyond passwords, companies are implementing new methods of authentication – from facial recognition to fingerprints. However, these technologies are still vulnerable and as such, the report anticipates that a new wave of companies will embrace multi-factor authentication to combat the assault on passwords and attacks targeting biometrics. This will require individuals to present several pieces of evidence to an authentication instrument. With the new need for multi-factor authentication, and consumer demand for unobtrusive layers of security, expect to see the implementation of behavioral biometrics.
Criminals will target transactions that use reward points as currency, spurring mainstream adoption of bug bounty programs: Companies beyond the technology, government, automotive and financial services sectors will introduce bug bounty platforms into their security programs. As criminals target transactions that use points as currency, businesses with loyalty, gift and rewards programs –such as airlines, retailers, and hospitality providers– will be the next wave of companies implementing bug bounty programs. As more organizations adopt the programs, they will require support from external experts to avoid introducing new risks with improperly configured programs.
Ransomware attackers get targeted; crypto currencies help ransomware industry flourish. In 2018, ransomware criminals will evolve their tactics. The reports predicts that attackers utilizing forms of benign malware—such as software designed to cause DDoS attacks or launch display ads on thousands of systems— will launch huge outbreaks of ransomware. While attackers will continue to launch scatter-gun-style attacks to disrupt as many systems as possible, the report predicts an increase in instances of attacks targeting specific companies and demanding ransomware payments proportional to the value of the encrypted assets. Crypto currencies will continue to support the flourishing ransomware industry overall, despite law enforcement becoming more advanced in their ability to trace attacks, for example through bitcoin wallets.
Insider risks plague organizations as they underestimate their severe vulnerability and liability while major attacks fly under the radar. In 2017, businesses under invested in proactive insider risk mitigation strategies, and 2018 will be no different. According to the report, a continued lack of security training and technical controls, coupled with the changing dynamics of the modern workforce, the full extent of cyber attacks and incidents caused by insiders will not become fully public. Many companies will continue to reactively responding to incidents behind closed doors and remain unaware of the true cost and impact of insider risk on the organization.
What is Cybersecurity Risk Management
Cyber Risk Management is the next evolution in enterprise technology risk and security for organizations that increasingly rely on digital processes to run their business. Risk management is a concept that has been around as long as companies have had assets to protect. The simplest example may be insurance. Life, health, auto and other insurance are all designed to help a person protect against losses. Risk management also extends to physical devices, such doors and locks to protect homes and autos, vaults to protect money and precious jewels, and police, fire and security to protect against other physical risks.
What is cybersecurity risk management?
Rather than doors, locks and vaults, IT departments rely on a combination of strategies, technologies and user education to protect an enterprise against cybersecurity attacks that can compromise systems, steal data and other valuable company information, and damage an enterprise’s reputation. As the volume and severity of cyber attacks grow, the need for cybersecurity risk management grows with it.
Cybersecurity risk management takes the idea of real world risk management and applies it to the cyber world. It involves identifying your risks and vulnerabilities and applying administrative actions and comprehensive solutions to make sure your organization is adequately protected.
Setting up your risk management system
Before setting up a cybersecurity risk management system, the enterprise needs to determine what assets it needs to protect and place a priority on. As the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) points out in its Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, there is no one-size-fits all solution. Different organizations have different technology infrastructures and different potential risks. Some organizations such as financial services firms and healthcare organizations, have regulatory concerns in addition to business concerns that need to be addressed in a cybersecurity risk management system. Cybersecurity should follow a layered approach, with additional protections for the most important assets, such as corporate and customer data. Remember that reputational harm from a breach can do more damage than the breach itself.
Risk management with CyberSecOp
Identity Services
Identity services help companies manage the explosion of digital identities and access to critical resources, both internal and cloud-based. In this age of digital transformation, the spheres of the individual’s life―as a professional, consumer, and private citizen―are interlinked in a complex digital structure, like a piece of fabric. The growing ability to piece together a digital picture of a person’s life and identity carries both risk and opportunity.
Wherever an organization is on its journey, we can help them achieve efficiencies, reduce risk, and evolve to support the changing needs of the digital business. With 20 years of identity management experience across the major industries, we offer field-tested accelerators and methods that are scalable and adaptive to each client’s specific set of business requirements.
Data Protection
Data Protection services help implement capabilities and technologies to protect sensitive data. As infrastructure and applications become more virtualized and adaptive, new cybersecurity gaps can be created as fast as old ones have been addressed, making the prevention of data breaches more difficult than ever. By prioritizing preventative and detective defenses around highly sensitive data, security teams can help reduce data loss and risk when attackers get past network, application, and infrastructure controls.
Leveraging these principles and an understanding of each client’s risk profile, CyberSecOp helps organizations design, implement, and manage capabilities to help better protect sensitive information across the end-to-end data lifecycle, and at an organization’s last line of defense.Application Security
In the era of digital transformation, application portfolios are becoming exponentially more diverse—and support a growing community of users. As the application “surface area” expands, so does cyber risk. Amid the change, one thing remains constant: applications are the lifeline of the business—and need to be a front line of cyber defense. It’s an important time for organizations to reexamine their approaches to application security.
Improving application security requires technical attention to individual applications, but also a broad framework across the application portfolio—from custom-developed to commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) applications and whether managed on-premise, on a mobile platform, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment. It also requires the flexibility to support varying and often coexisting system methodology processes from waterfall, to agile, to DevOps in order to address application-related cyber risk at the pace of the organization’s digital evolution.
CyberSecOp’s application security services help organizations to design and implement security mechanisms across the system development methodology that can flex to your operational requirements to drive value through IT while also protecting your application portfolio against the changing cyber threat landscape.Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure Security services focus on developing advanced protection of core systems and devices. Today’s critical business drivers—the need to digitally transform, modernize the supply chain, enhance customer experience, increase agility, reduce costs, etc.—are driving a major shift in technology priorities. This shift includes increasing focus on cloud adoption, the Internet of Things (IoT), hybrid computing, software-defined networks (SDN), robotic process automation (RPA), blockchain, artificial intelligence, and more. The infrastructure supporting it has become highly virtualized and automated—and the traditional means of securing infrastructure fall short.
CyberSecOp helps organizations move toward a modernized, risk-focused agile defense approach. While the basic infrastructure domains—physical facilities, networks, systems and storage, and endpoints—that need to be protected remain the same, the means to secure them must evolve. By providing assessment, strategy, architecture, implementation, and operational management assistance across the four infrastructure domains, we help clients face our brave new world with a transformed, agile defense capability.
Data Protection Solutions & Data Security
Protect and secure data and data privacy is critical since most companies hold clients/costumers sensitive data, and protect that data is not only critical to its clients/costumes. Data protection is also critical for companies intellectual properties and reputation.
Data Protection Services
As more organizations move to hybrid or multi-cloud IT strategy, managing data protection services has become increasingly more complex. Various systems, technologies and environments require different tools for data protection management, and many IT teams find they must use a variety of tools to perform backup operations. In addition to greater inefficiency and rising costs, this intensive focus on data protection services diverts IT teams from higher value tasks and other strategic priorities.
Data Protection Simplified by CyberSecOp LocVault services
To simplify data protection services, CyberSecOp offers a Managed Data Protection solution that can protect digital assets across all your environments. Powered by Locvault's best-in-class data backup and recovery software, CyberSecOps Managed Data protection services help simplify data protection by enabling IT teams to use a single tool for backup and restore processes.
Efficiently Protect, Manage and Recover Your Data
Protect, manage and access the information you need with a heterogeneous data protection solution
A single interface manages data at a fraction of the time, effort and cost required by separate point products
Simplify data management in complex networked storage environments with a consistent way to locate and manage data and applications
With Privacy and Data Protection, CyberSecOp LocVault will help you protect your sensitive business data and help you meet compliance requirements related to data storage and protection.
We’ll also help you assess your risk, create custom policies to encrypt and restrict access to sensitive data, and report on data access — helping to ensure that your important data remains protected. Speak with an expert
Are Users Your Weakest Link - To Your Cybersecurity Posture
Humans remain the weak link in corporate data protection
Humans remain the weak link in corporate data protection, but you might be surprised that it isn't only rank-and-file employees duped by phishing scams who pose risks. Some companies are lulled into a false sense of cybersecurity by vendors. You read that right, Some enterprises believe the shiny new technologies they've acquired will protect them from anything.
As we continue to build defense in depth and deploy security appliances utilizing AI and other emerging technologies, attackers will continue to pivot to the perennial weak spot: the users. Recently I hosted the Social Engineering Capture The Flag competition at Hackfest in Quebec, and similar to last year, the results were sobering. Every single targeted company had employees that gave detailed information over the phone on their OS and service pack level, and 88 percent gave detailed information on the browser they were using. Three quarters went to a URL that they were given over the phone. The information that the companies bled was disheartening but not shocking. Until we train employees to trust their instincts and tell them it's okay to say no to a customer, things won't change. In the current environment where companies ask their customers to leave a positive review online, employees increasingly feel less empowered to terminate a call they feel is suspicious. Your friendly neighborhood hacker is happy to exploit this weakness.
Billions being send on security tools
The threat of cyber crime has created a significant increase in interest on the topic of cyber security, with organizations spending billions of dollars to protect themselves against a fast evolving array of current and potential future threats. Many spend heavily on monitoring, surveillance and software; however, they often neglect the risk exposure created by their own people – and, in this digital age, by their customers.
Businesses are losing the fight, pay ransom, or lose their lively hood
Businesses are forced to make exceedingly difficult decisions. On one hand, it feels wrong to negotiate with the cybercriminals and give them what they want. On the other hand, the looming financial hit and business interruption is typically far more detrimental than the payoff amount. If business owners don’t engage with the ransomers, they face the prospect that they, and their employees, may lose their livelihood. I see ransomware as a continuing cyber threat in 2019 and beyond. It’s up to business owners to implement the best security practices and ensure that their employees are properly trained to identify and avoid potential threats.
Choosing A Managed Detection & Response Provider
Why Managed Detection & Response Provider may be the right move
Companies outsourcing security need Managed Detection & Response providers (MDR) more than ever to improve cyber resilience. With the security landscape growing more complex, and the costs of maintaining adequate in-house security teams high, it makes sense for many companies to outsource the tasks of threat hunting and response to ensure that they can promptly identify potential threats and react swiftly to mitigate damages. Managed Detection & Response providers often integrate tools such as Endpoint Detection & Response and other solutions to detect threats, analyze risk, and correlate threat data to pinpoint patterns that could indicate a larger attack.
How to choose the right Manged Detection & Response Provider
Smart moves: you’re making them. How do we know? For one, you’re investigating ways to close the gaps in your threat detection and incident response. Which makes sense, given that assembling the talent and tech to thoroughly thwart attackers requires more than most organizations can commit to. Even smarter, you’re checking out Managed Detection and Response (MDR) Services, an increasingly popular solution which combines expertise and tools to provide monitoring and alerting, as well as remote incident investigation and response that can help you detect and remediate threats.
9 things to look our for when choosing a Managed Detection & Response Provider
Your Managed Detection & Response Provider should combine numerous data inputs from security detection tools, threat intel feeds, third party data sources, and the IT asset database to identify not only where there is a threat but its risk compared to others in the queue.
Assess your company's present and future technology needs and initiatives. Qualify, quantify and communicate those needs throughout your company. Is the Managed Detection & Response Provider able to address your range of needs?
Technology strategies should encompass people and processes as part of the organization's mission and strategies. Do they offer ongoing employee training as part of their service?
Does the Managed Detection & Response Provider continuously assess your organization's performance for meeting objectives? You want a partner that focuses on continuous evaluation and improvement of your objectives.
Review your company's goals and mission. Ensure they are clear and concise and can be communicated to all organizational stakeholders as well as your new IT partner.
Perform annual policy and process reviews to assess organization's readiness for external reviews and incident response.
Identify and create teams within your organization to define current challenges and align initiatives to those challenges.
Through playbooks and pre-defined workflows, you can quickly assess and begin to remediate security incidents based on best practices. Ask a Managed Detection & Response Provider if they include such materials as part of their package.
CIOs/CISOs should have unprecedented transparency to all aspects of the security environment. Through dashboards and visualization techniques, CIOs/CISOs will be more easily able to communicate with Managed Detection & Response Providers which vulnerabilities and threats exist and the risks of inaction.
What is Regulatory Compliance & Services?
What is Compliance
Compliance means conforming to a rule, such as a specification, policy, standard or law. Regulatory compliance describes the goal that organizations aspire to achieve in their efforts to ensure that they are aware of and take steps to comply with relevant laws, policies, and regulations.
Business and Compliance
When it comes to a business and corporate management, compliance refers to the company obeying all of the legal laws and regulations in regards to how they manage the business, their staff, and their treatment towards their consumers. The concept of compliance is to make sure that corporations act responsibly.
The pressure to comply with constantly changing regulatory, third-party, and internal guidelines can be overwhelming. Being unprepared to manage risks yet meet mandates can lead to economic consequences and legal liabilities. Both can contribute to a significant financial impact and hurt to your reputation, which could prove even more damaging. You may be exposed to threats you’re not yet familiar with that could be putting your company’s reputation at risk—and even jeopardizing its future.Many major companies within the United States are subject to some type of security regulation.
Complying to regulatory compliance
Regulations that contain information security requirements are intended to improve the information security level of organizations within that industry and many organizations would welcome such information. The difficulty comes in determining which regulations apply and in interpreting the requirements of the regulation. The regulations are not written in a way that is easily understood by the average business person so many times a security professional is needed to understand the requirements and how to best implement them. Professionals have experience implementing systems, policies, and procedures to satisfy the requirements of the regulation and enhance the security of your organization and some have obtained credentials such as (CyberSecOp Information Security Practitioner) that signify their understanding of the regulations. Often the requirements are given in general terms leaving the company to determine how to best satisfy the requirements.
For those organizations without a robust security department, we provide a Virtual CISO offering with expertise in the following:
ISO 27001/27002
NIST & NIST Cybersecurity
GDPR
CCPA
FedRamp
NY DFS Requirements 23 NYCRR 500
FFIEC Handbook
FERPA
HIPAA/HITECH
Hi-Trust
PCI-DSS
Phishing Attack Prevention: What is Phishing?
What is Phishing?
Phishing is the practice of sending fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable source. It is usually done through email. The goal is to steal sensitive data like credit card and login information, or to install malware on the victim’s machine. Phishing is a common type of cyber attack that everyone should learn about to protect themselves.
Phishing Attack Prevention:
Why are so many companies vulnerable to phishing? Not having the right tools in place and failing to train employees on their role in information security.
Employees possess credentials and overall knowledge that is critical to the success of a breach of the company's security. One of how an intruder obtains this protected information is via phishing. The purpose of phishing is to collect sensitive information to use that information to gain access to otherwise protected data, networks, etc. A phisher's success is contingent upon establishing trust with its victims. We live in a digital age, and gathering information has become much easier as we are well beyond the dumpster diving days.
How do I protect against phishing attacks?
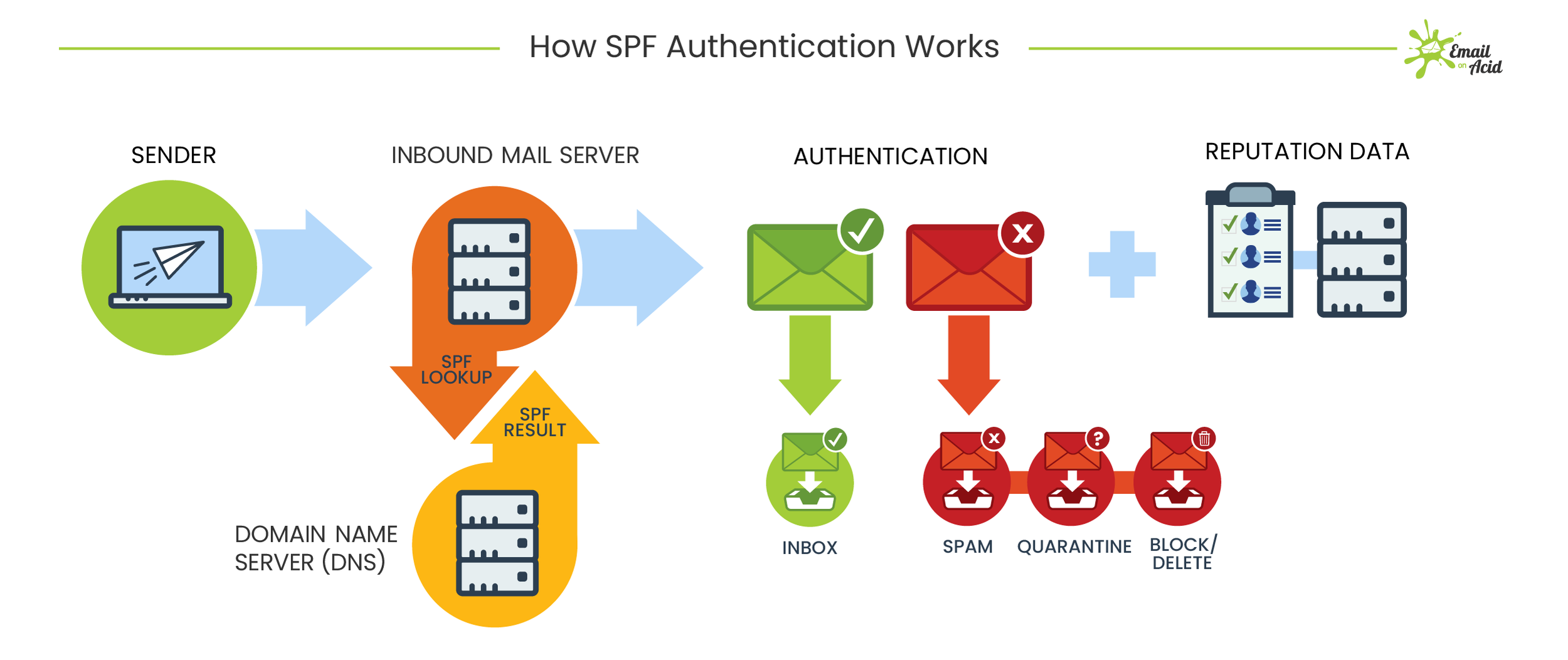
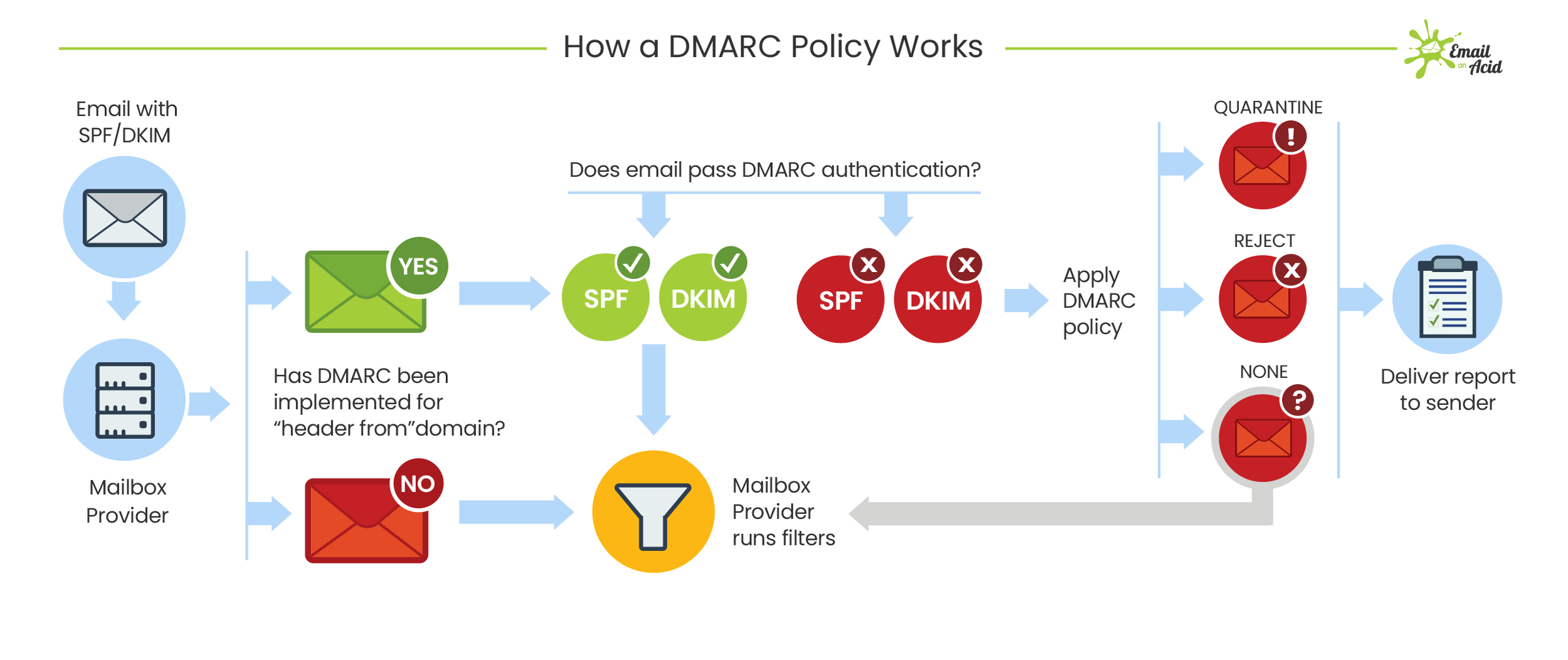
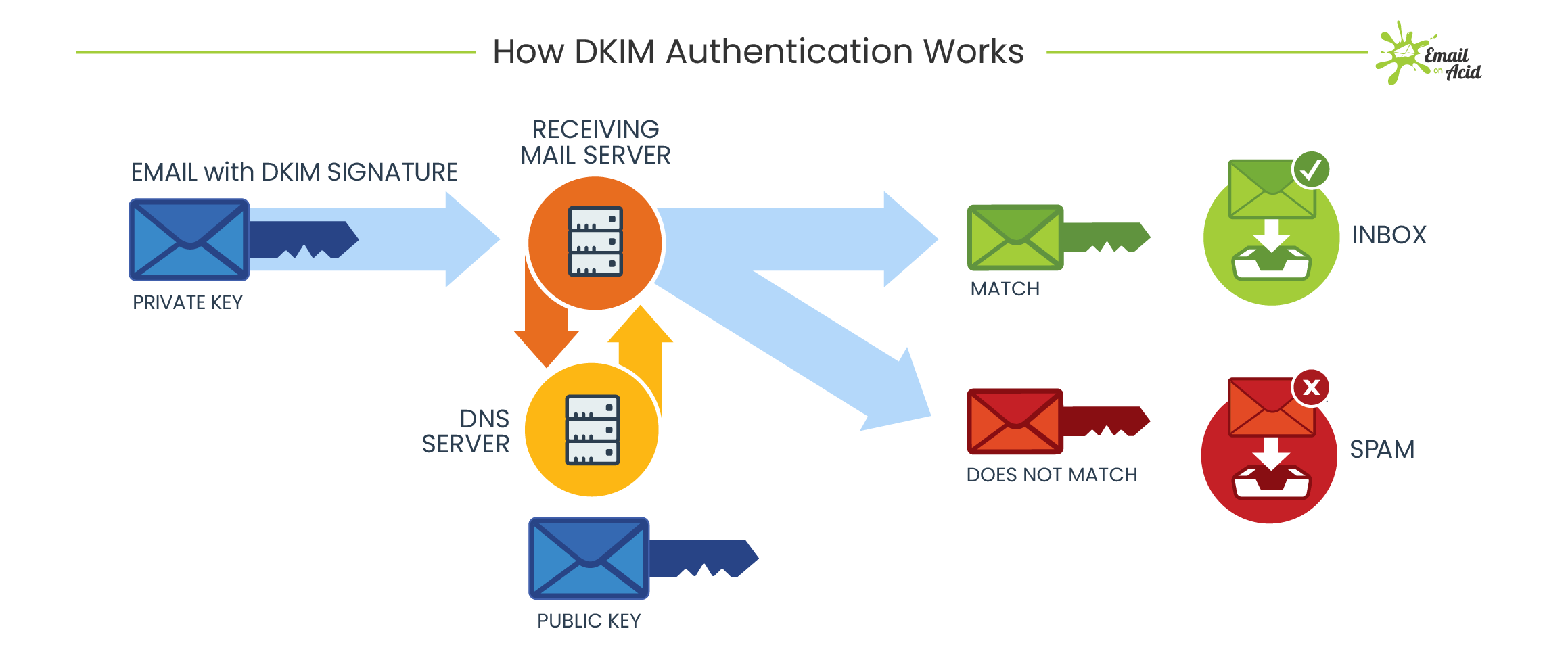
Free Email Protection
Free protocols that help organizations improve email security; Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) were developed. SPF cross-checks the sender’s IP address with an approved list of IP addresses, and DKIM uses an encrypted digital signature to protect emails. While these are both individually effective, they have their own set of flaws. DMARC, developed in 2012, is a protocol that uses both SPF and DKIM authentication to secure email and has a mechanism that sends the domain owner a report whenever an email fails DMARC validation.
But here’s the thing: a recent report from phishing specialist Agari states that only 1/3 of the Fortune 500 have configured DMARC.
User education
One way to protect your organization from phishing is user education. Education should involve all employees. High-level executives are often a target. Teach them how to recognize a phishing email and what to do when they receive one. Simulation exercises are also key for assessing how your employees react to a staged phishing attack.
Security technology
No single cybersecurity technology can prevent phishing attacks. Instead, organizations must take a layered approach to reduce the number of attacks and lessen their impact when they do occur. Network security technologies that should be implemented include email and web security, malware protection, user behavior monitoring, and access control.
How does phishing work?
Phishing starts with a fraudulent email or other communication that is designed to lure a victim. The message is made to look as though it comes from a trusted sender. If it fools the victim, he or she is coaxed into providing confidential information, often on a scam website. Sometimes malware is also downloaded onto the target’s computer.
What are the dangers of phishing attacks?
Sometimes attackers are satisfied with getting a victim’s credit card information or other personal data for financial gain. Other times, phishing emails are sent to obtain employee login information or other details for use in an advanced attack against a specific company. Cybercrime attacks such as advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware often start with phishing.
Types of Phishing
Deceptive Phishing. The term "phishing" originally referred to account theft using instant messaging but the most common broadcast method today is a deceptive email message. Messages about the need to verify account information, system failure requiring users to re-enter their information, fictitious account charges, undesirable account changes, new free services requiring quick action, and many other scams are broadcast to a wide group of recipients with the hope that the unwary will respond by clicking a link to or signing onto a bogus site where their confidential information can be collected.
Malware-Based Phishing refers to scams that involve running malicious software on users' PCs. Malware can be introduced as an email attachment, as a downloadable file from a web site, or by exploiting known security vulnerabilities--a particular issue for small and medium businesses (SMBs) who are not always able to keep their software applications up to date.
Keyloggers and Screenloggers are particular varieties of malware that track keyboard input and send relevant information to the hacker via the Internet. They can embed themselves into users' browsers as small utility programs known as helper objects that run automatically when the browser is started as well as into system files as device drivers or screen monitors.
Session Hijacking describes an attack where users' activities are monitored until they sign in to a target account or transaction and establish their bona fide credentials. At that point the malicious software takes over and can undertake unauthorized actions, such as transferring funds, without the user's knowledge.
Web Trojans pop up invisibly when users are attempting to log in. They collect the user's credentials locally and transmit them to the phisher.
Hosts File Poisoning. When a user types a URL to visit a website it must first be translated into an IP address before it's transmitted over the Internet. The majority of SMB users' PCs running a Microsoft Windows operating system first look up these "host names" in their "hosts" file before undertaking a Domain Name System (DNS) lookup. By "poisoning" the hosts file, hackers have a bogus address transmitted,taking the user unwittingly to a fake "look alike" website where their information can be stolen.
System Reconfiguration Attacks modify settings on a user's PC for malicious purposes. For example: URLs in a favorites file might be modified to direct users to look alike websites. For example: a bank website URL may be changed from "bankofabc.com" to "bancofabc.com".
Data Theft. Unsecured PCs often contain subsets of sensitive information stored elsewhere on secured servers. Certainly PCs are used to access such servers and can be more easily compromised. Data theft is a widely used approach to business espionage. By stealing confidential communications, design documents, legal opinions, employee related records, etc., thieves profit from selling to those who may want to embarrass or cause economic damage or to competitors.
DNS-Based Phishing ("Pharming"). Pharming is the term given to hosts file modification or Domain Name System (DNS)-based phishing. With a pharming scheme, hackers tamper with a company's hosts files or domain name system so that requests for URLs or name service return a bogus address and subsequent communications are directed to a fake site. The result: users are unaware that the website where they are entering confidential information is controlled by hackers and is probably not even in the same country as the legitimate website.
Content-Injection Phishing describes the situation where hackers replace part of the content of a legitimate site with false content designed to mislead or misdirect the user into giving up their confidential information to the hacker. For example, hackers may insert malicious code to log user's credentials or an overlay which can secretly collect information and deliver it to the hacker's phishing server.
Man-in-the-Middle Phishing is harder to detect than many other forms of phishing. In these attacks hackers position themselves between the user and the legitimate website or system. They record the information being entered but continue to pass it on so that users' transactions are not affected. Later they can sell or use the information or credentials collected when the user is not active on the system.
Search Engine Phishing occurs when phishers create websites with attractive (often too attractive) sounding offers and have them indexed legitimately with search engines. Users find the sites in the normal course of searching for products or services and are fooled into giving up their information. For example, scammers have set up false banking sites offering lower credit costs or better interest rates than other banks. Victims who use these sites to save or make more from interest charges are encouraged to transfer existing accounts and deceived into giving up their details.
CEOs and Cyber Security: are they the road block?
CEOs and cybersecurity: are they the road block?
Senior executives may be the weakest link in the corporate cyber security chain and are a primary target of hackers, fraud and phishing scams, says report. it also should be know that the are the road block to approve budget for information security, and most often security takes back sit to profit.
Report by many source and research done by many firm identity senior executive has the road block to good security within their firms, Many CEOs think they are immune to hackers, at least that’s what a new report According to the report, these findings are ironic given that CEOs are the ideal victim.
Senior Executive Are You the Weakest Link?
According to the report, Are You the Weakest Link? How Senior Executives Can Avoid Breaking the Cybersecurity Chain, many senior executives ignore the threat from hackers and cyber criminals and often feel that security policies in their respective organisations do not apply to their unique position.
In reality, their often privileged access to company information makes their personal accounts extremely valuable to exploit and heightens the need for extra care.
Professional hackers and adversaries will usually do a thorough investigation into a senior executive or board level director, including full analysis which could entail in-depth monitoring of the company website and associated social media accounts (including employees and their extended networks).
It appears that many CEOs commonly view cyber security as a responsibility for the IT department only. In reality, IT security has now become a remit for all individuals.
“All employees — especially those at the top of the corporate ladder — need to realise that cybercriminals use social engineering, email phishing and malware to access personal accounts, and C-level staff especially need to avoid becoming the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain by adhering to regularly updated, company-wide security policies regarding data sharing and backup,”
“Reviewing corporate policies, with a focus on people, premises, processes, systems and suppliers will provide valuable insights into which areas to improve, and by championing a ‘security first’ corporate culture, organisations and their senior executives will be well positioned to avoid the high financial costs, reputation damage and unexpected downtime that could result from a cyberattack or data breach.”
Cloud Security - Cloud Cyber Security
Cloud Security - Cloud Cyber Security
Of the large amount of data that has been moved to the cloud, a huge segment of it has been compromised. The compromised data includes election data, financial information like bank cards, health data, etc. Maintaining integrity and security continues to be a significant challenge for cloud platforms. [3]
In an attempt to provide extra security for cloud data, many cloud service providers (CSPs), have launched extensive cloud security technologies. Google has announced ‘shielded VMs’ to prevent hostile attacks. Even with these security technologies in place, however, users still have a large role to play in keeping their data safe.
In many cases, IT teams have recognized the lack of control when data is placed in the cloud. This lack of control is a symptom of the absence of an overarching security strategy. The challenge presents itself when an organization transfers data to the CSPs without maintaining any additional backup, as this could result In the loss of data at times. Stressing on the importance to maintain an additional backup of data. [3]
Another common challenge with the cloud is the unclear point-to-point access. Access permissions are complicated when an organization’s data is placed on a third-party cloud server. Planning and strategizing the access controls around crucial data is as important as defining the access points and control measures. Security in the cloud is different from on-premises security, making it complex due to the various rules implemented and security issues faced, such as failure to encrypt data. Access to the cloud server should be defined on a point-to-point basis. That means that access to data should be restricted based on the requirement of every individual, whether management or staff, should be clearly defined. A flow chart explaining the access points should be shared with the CSP to bring them on equal understanding to avoid conflicts.
Securing Your Data on the Cloud
The main objective of cloud security is to keep data secure, sharing the responsibility between the provider and the client. Here are some good practices that can be implemented to leverage the benefits of cloud services.
a) Encryption of Data
End-to-end encryption of data in transit
For high-security processes, where the data is highly confidential, all interactions with servers should happen over a secure socket layer (SSL) transmission. To ensure the end-to-end encryption of data, the SSL should terminate within the CSP’s network. Comprehensive encryption, when performed at the file level, makes cloud security stronger. All data should be encrypted before being uploaded to the cloud.
Encryption of data when at rest
Even when data is at rest, encryption should be enabled. This helps in complying with regulatory requirements, privacy policies, and contractual obligations related to confidential data. Before registering with your CSP, security policies should be verified with an auditor. AES-256 is used for encrypting data in the cloud and the keys should be encrypted with master keys in the rotation. Field-level encryption will also help keep the data secure.
b) Robust and Continuous Vulnerability Testing and Incident Response
A good CSP contract includes regular vulnerability assessment and incident response tools that extend to devices and networks. The solutions given by incidence response tools might enable automated security assessments to test system weaknesses. CSPs should be able to perform scans on demand.
c) End-user Device Security
Securing cloud-connected end-user devices is an often-overlooked component of a well-rounded security program. When utilizing infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) or platform-as-a-service (PaaS) models, deploying firewall solutions in your end devices to protect the network perimeter is very important.
d) A Private Cloud and Network are Best
Opting for a cloud environment which is private and where you can have complete control over access to your data is the preferred method as opposed to using a multi-tenant instance. Also, opt for cloud storage or software-as-a-service (SaaS) which belongs to only you and is not shared with others. These personal clouds are called virtual private clouds (VPC) and all traffic to and from these VPCs can be routed to the corporate data center. This can be done through an internet protocol security (IPsec) hardware VPN connection.
e) Compliance Certifications
The two most important certifications that you should consider are SOC 2 Type II and PCI DSS.
SOC 2 Type II is a type of regulatory report that defines the internal controls of how a company should safeguard its customer data and operation controls. SOC2 deals with regulatory compliance, internal risk management processes, and vendor management programs. It confirms that a cloud service has robust management as it is specifically designed to ensure higher standards of data security.
PCI DSS – PCI DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard and is important to organizations that deal with credit card transactions. Meeting this standard helps keep cardholder data safe from fraud. It ensures that sensitive data stored in a cloud is processed and transmitted in a secure manner. It impacts security policies, procedures, software design, network architecture, and various protective measures.
Leading public cloud providers like Microsoft and Amazon offer proprietary credential management tools to provide legitimate access and keep intruders away from sensitive data. Having sophisticated tools can help ensure the security of your data in the cloud.
Defense is a matter of strict design principles and security policies scattered over various departments. By implementing the above key guidelines as part of your cloud strategy, you are on your way to securing your data in the cloud.
Ethical Hacker for Secure Cloud Storage
An ethical hacker is a skilled trained professional who knows how to locate the vulnerabilities in target systems, including cloud storage platforms and networks. The term ‘ethical’ differentiates a black-hat hacker from a white-hat hacker.
CCPA Data Privacy - California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
CCPA Data Privacy
The California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) into effect. This new consumer privacy law comes post Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and, for some, is seen as a smaller version – without the option to opt-out of data collection all-together that the GDPR has.
CCPA is a consumer privacy law that will be coming into effect on January 1, 2020. The bill – which is aggressive for American privacy policy standards – will put guidelines on personal information collection and post-data-acquisition data usage by businesses.
Come 2020, the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”) may significantly impact businesses’ data practices, with new and burdensome compliance obligations such as “sale” opt-out requirements and, in certain circumstances, restrictions on tiered pricing and service levels. The breadth of personal information covered by the CCPA, going beyond what is typically covered by U.S. privacy laws, will complicate compliance and business operations.
Who need to comply with CCPA
Companies, especially those outside of California, may wonder whether they are subject to the CCPA. CCPA applies to for-profit entities that (1) have greater than $25 million in gross annual revenues; (2) annually handle personal information of 50,000 or more consumers, households, or devices; or (3) derive 50% or more of annual revenue from selling personal information. These criteria will result in a wide swath of businesses being subject to the CCPA. For example, a website might only need 137 unique visitors from California per day to reach the threshold of 50,000 consumers. That website’s collection of data through cookies may be captured by the CCPA’s broad definition of personal information. And given the third criterion focused on revenue percentage, even very small businesses that regularly exchange data, for example in the online ecosystem, might be captured if their activities are deemed to be a “sale” under the CCPA.
CCPA PRIVACY OVERSIGHT
The CCPA will impose substantial compliance obligations on all businesses that handle personal information of California consumers. Such obligations may pose particular challenges for the ever increasing array of businesses that leverage consumer data for analytics, profiling, advertising, and other monetization activities, particularly as the compliance requirements are not easily gleaned from the statutory language. Addressing these challenges will require creative, thoughtful approaches and may potentially involve industry-wide coordination to develop and advance practical solutions.
CyberSecOp CCPA privacy consultants incorporates your CCPA compliance requirements, powered by a unique combination of deep privacy expertise developed over two decades, proven methodologies refined through tens of thousands of engagements, and powerful technology operating at scale for 20 years.
WHAT DO SECURITY CONSULTANTS DO?
WHAT DO SECURITY CONSULTANTS DO?
Security consults deal with various threats to physical and computer security. Security threats come in many forms such as computer hackers, terrorists, and attacks on physical assets. There are specializations for security consultants of building security, natural and man-made disaster prevention, or with computer security issues.
Some of the roles security consultants may do for companies or private individuals are installing physical protections of video surveillance and alarm systems. Physical security risks are issues for many companies and security consultants may determine physical security risks such as threats of violence in the workplace, the stability of a building during tornadoes, earthquakes, fires, or other natural disasters, and development of evacuation plans for personnel during emergencies. Security consultants also may advise on building maintenance issues.
What services does a security consultants provide?
Security consultants can also help to incorporate security changes at all levels of the company. Based upon the security audit that’s conducted, a security consultant, if allowed to, can implement various new security measures and procedures throughout the company, which can include security related to:
Analyzing areas that are currently exposed and if they have had their security compromised in the past;
Performing a gap analysis in order to determine if any areas of a company’s current security does not meet accepted industry standards;
Gauging the work environment through performing interviews with important personnel and company employees;
Providing a list of recommendations based upon found security vulnerabilities, which includes security measures that should be incorporated.
Policies and procedures;
Electronic surveillance and alarm systems;
Security personnel.
A security consultant will work closely with management for the purposes of transparent communication and to make sure that any security changes that are implemented are done so within the allotted budget. The degree to which a security consultant can incorporate security changes depends largely upon this, in addition to the management’s instructions.
CyberSecOp Security Services has been providing expert security consulting services for decades. Make sure to contact us today to ask about our advanced security consulting services, which will be personalized to your company’s particular needs.
HHS voluntary healthcare cybersecurity practices
The Department of Health and Human Services has released voluntary cybersecurity practices to the healthcare industry to move organizations “towards consistency” in mitigating cyber threats.
According to HHS, the four-volume publication guides “cost-effective methods that a range of healthcare organizations at every size and resource level can use to reduce cybersecurity risks.” It is meant to raise awareness of cyber threats and provide vetted practices.
“Cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility—it is the responsibility of every organization working in healthcare and public health,” says HHS Acting Chief Information Security Officer Janet Vogel. “In all of our efforts, we must recognize and leverage the value of partnerships among government and industry stakeholders to tackle the shared problems collaboratively.”
HHS Headquarters in Washington, D.C.
Mandated by the Cybersecurity Act of 2015, HHS convened more than 150 cyber and healthcare experts from government and industry to develop the recommended practices as part of the Healthcare and Public Health Sector Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience Public-Private Partnership.
“The healthcare industry is truly a varied digital ecosystem—we heard loud and clear through this process that providers need actionable and practical advice, tailored to their needs, to manage modern cyber threats,” says Erik Decker, industry co-lead and chief information security and privacy officer at the University of Chicago Medicine. “That is exactly what this resource delivers; recommendations stratified by the organization's size, written for both the clinician and the IT subject matter expert.”
In addition to the main document, which lays out the five most relevant and current threats to the industry, the publication also recommends ten cybersecurity practices to help mitigate these threats. It also includes two technical volumes geared for IT and security professionals: Technical Volume 1 focuses on cybersecurity practices for small healthcare organizations. In contrast, Technical Volume 2 focuses on techniques for medium and large healthcare organizations.
Cyber Security Do's and Don'ts
Information and Cyber Security Consulting Services: Cyber security systems and principles are designed to safeguard company data, websites and web applications from attackers seeking to disrupt, delay, alter or redirect the flow of data. These attackers vary in target, motive, levels of organization, and technical capabilities, requiring public and private organizations to adopt ever-increasing measures to prevent cyber attacks. CyberSecOp is an award winning US based to Cyber Security Consulting Company.
The following are some important do’s and don’ts for advisers to keep in mind when executing on the action steps in your cybersecurity plan:
Make use of all tools available from your broker-dealer or custodian. The securities industry is investing tens of millions of dollars in cybersecurity, making tools and resources available to advisers and their teams. Actively seek out those tools and become known at your firm for your interest in and commitment to cybersecurity.
Eliminate weak links in your system. Hackers will be turned away from your systems that use strong passwords and encryption. Don’t let users share passwords. In addition to PCs, encrypt
all thumb drives, cell phones and tablets. And set untended computers to lock automatically after a set number of minutes.
Take preparation, training and review seriously. Put effort into your plan, review it seriously on a regular basis, document that review, and make sure that all staff – including even those who don’t usually deal with clients or their information – are regularly trained and updated on cybersecurity policies and procedures. Since staff carelessness or inattention can be the weakest link
in the defense chain, make sure that you and your staff never download an attachment or accept a request if it can’t be verified.
Be alert to things that don’t feel right. Suppose, for example, that a staff member receives a phone call from someone saying he’s from Microsoft tech support and has noticed a computer virus on your system. Even if the employee isn’t aware that reputable tech support operations don’t work that way, he or she should immediately sense that the call is out of the ordinary and somehow amiss. Given that feeling, the employee should hang up immediately and not let the unidentified caller connect to the firm’s system. Similarly, if you or staff receive an e-mail from a client saying they’ve been mugged on vacation or have lost their wallet or passport, most likely their e-mail has been hacked. Contact that person via landline or cell phone and confirm the story.
Educate your users and clients in how to communicate safely. Advisers should require multifactor authentication (use of a token or other identifier beyond password or ID) for client communication through Gmail, Yahoo! and other major providers. This will protect them, and you, from hackers.
Don’t keep cybersecurity a secret. The financial advice business is competitive, but there is one area where cooperation, not competition, is paramount: cybersecurity. Discuss the issue frequently with peers and share any ideas you have.
Don’t lull yourself into thinking cybersecurity is someone else’s problem. Be alert to news and developments in cybercrime and cybersecurity and seek more information and update plans and programs accordingly. Start by identifying your three biggest potential threats and get to work addressing them.
HIPAA Modernization of Security Standards
HIPAA Modernization of Security Standards
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, better known (if not always spelled correctly) as HIPAA, was signed into law by President Bill Clinton in August 1996.
A lot has changed in the two decades since – in the ways consumers interact with health systems and the ways technology is transforming care delivery and the patient experience. So maybe it's time to give the privacy law a refresh, said the American Medical Informatics Association and the American Health Information Management Association.
WHY IT MATTERS
As access to personal health information is easier than ever, with smartphones now ubiquitous and apps and connected devices proliferating by the day, both AMIA and AHIMA have voiced support for HIPAA modernization.
In a joint appearance on Capitol Hill, in a presentation about unlocking data for patient empowerment, experts from the two groups highlighted how healthcare has a lot of catching up to do to serve a population used to online shopping, travel booking, review sites and more.
Webinar: The Future of Medicine: Protecting Privacy Without Impacting Quality of Care
Toward this vision of improved patient experience, AMIA and AHIMA said U.S. policymakers should take steps to update HIPAA to enable greater data access and portability – something that looks more likely than it did even a few months ago.
It could be done in a couple different ways, they said. First, potentially, by establishing a new concept of a health data set, with that HDS comprising all the clinical, biomedical and claims data maintained by a covered entity or business associate.
Another option is to revise HIPAA's existing "designated record set" definition, requiring certified health IT products to provide that amended DRS to patients digitally – enabling in a way that enables them to use and reuse their data.
They explained that a new definition for HDS would support individual HIPAA right of access and guide the future development of ONC's Certification Program so individuals could view, download, or transmit to a third party this information electronically and access this information via application programming interface.
Revising the existing DRS definition, meanwhile, offer more clarity and predictability for both providers and patients, AMIA and AHIMA said.
THE LARGER TREND
Even as the availability and maturity of consumer technology has improved, "more than two decades after Congress declared access a right guaranteed by law, patients continue to face barriers," said Dr. Thomas Payne, medical director, IT Services at UW Medicine. "We need a focused look at both the technical as well as social barriers."
AMIA and AHIMA called a broader conversation regarding consumer data privacy, and called on Congress to "extend the HIPAA individual right of access and amendment to non-HIPAA Covered Entities that manage individual health data, such as mHealth and health social media applications. The goal is uniformity of data access policy, regardless of covered entity, business associate, or other commercial status."
Moreover, the groups said regulators should clarify existing regulatory guidance related, for example, to third-party legal requests, such as those by lawyers looking for information without appropriate patient permissions.
ON THE RECORD
"Congress has long prioritized patients' right to access their data as a key lever to improve care, enable research, and empower patients to live healthy lifestyles," said Dr. Doug Fridsma, president and CEO and AMIA. "But enacting these policies into regulations and translating these regulations to practice has proven more difficult than Congress imagined."
"AHIMA's members are most aware of patient challenges in accessing their data as they operationalize the process for access across the healthcare landscape," said AHIMA CEO Wylecia Wiggs Harris, in a statement. "The language in HIPAA complicates these efforts in an electronic world."