CYBER SECURITY CONSULTING SERVICE AWARDS AND RECOGNITIONS
CyberSecOp's comprehensive managed security services, cyber security consulting, professional services, and data protection technology are recognized as industry-leading threat detection and response solutions by major analyst firms, key media outlets, and others.
Hackers Now Utilizing Standard Tools in Data Breaches
Several significant developments have emerged in today's dynamic cybersecurity landscape, highlighting threat actors' evolving tactics and the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Firstly, the emergence of ShrinkLocker, a ransomware variant exploiting Windows BitLocker, underscores cybercriminals' adaptability in leveraging built-in encryption features for malicious purposes.
Secondly, pharmacy benefit management company Sav-Rx's disclosure of a data breach affecting 2.8 million Americans underscores the ongoing challenges in safeguarding sensitive personal and medical information.
Standard tools are now being employed against organizations, as hackers no longer need to develop or learn new techniques, all while evading detection. This trend has significantly reduced the time required to execute a successful attack, particularly because most organizations rely on well-known software.
1. Ransomware Exploits Windows BitLocker
A new strain of ransomware, dubbed ShrinkLocker, has surfaced. It leverages the Windows BitLocker feature to encrypt victim data. Threat actors are manipulating BitLocker, a full-volume encryptor integrated into the Windows operating system, to encrypt entire hard drives, rendering data inaccessible. Researchers from Kaspersky have identified this new threat, highlighting the importance of robust cybersecurity defenses.
2. Sav-Rx Discloses Data Breach
Pharmacy benefits management company Sav-Rx has disclosed a data breach affecting 2.8 million Americans. The cyberattack, which occurred last October, resulted in the theft of personal data, including sensitive medical information. Investigations into the breach have been ongoing for eight months, underscoring the complex nature of cyber incidents and the importance of timely detection and response.
3. New ATM Malware Poses Global Threat
A new strain of ATM malware has been advertised on the dark web, claiming to compromise a significant percentage of ATMs worldwide. Targeting machines from leading manufacturers, including Diebold Nixdorf and NCR, the malware seriously threatens financial institutions and consumers. The availability of a three-day trial further underscores the sophistication of cybercriminal tactics.
4. Phishing Campaigns Targets Finance Companies
A phishing campaign employing a Python clone of the popular game Minesweeper has surfaced, targeting finance companies in Europe and the U.S. The campaign utilizes malicious scripts hidden within the game code to install remote management software, granting threat actors access to compromised systems. Vigilance against phishing attempts remains essential in mitigating cyber risks.
5. High-Severity Vulnerability Affects Cisco Firepower Management Center
Cisco has issued a warning regarding a high-severity vulnerability in the web-based management interface of the Firepower Management Center (FMC) Software. Exploitable via SQL injection, the vulnerability poses a significant risk to organizations using Cisco's security solutions. Immediate action is advised to mitigate potential exploitation.
6. Recovery Efforts Continue at Ascension Following Cyberattack
Healthcare network Ascension is gradually recovering from a recent cyberattack, which disrupted operations across its 140 member hospitals and senior care centers. The incident underscores the critical importance of cybersecurity in safeguarding patient care and sensitive medical information. Despite ongoing recovery efforts, challenges persist, highlighting the far-reaching impact of cyber incidents on healthcare organizations.
7. Courtroom Recording Software Compromised with Backdoor Installer
Justice AV Solutions (JAVS), a widely used technology for recording courtroom proceedings, has been compromised by hackers. A backdoor installer implanted in a software update allows threat actors to gain complete control of systems, posing significant privacy and security risks. Organizations utilizing JAVS technologies are advised to address the security issue and mitigate potential threats immediately.
Stay informed and proactive about evolving cyber threats. Cybersecurity remains a top priority for safeguarding digital assets and maintaining trust in an increasingly interconnected world.
In summary, the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, presenting complex challenges for organizations and individuals alike. By remaining vigilant, proactive, and leveraging robust cybersecurity solutions, stakeholders can effectively mitigate risks and safeguard against emerging threats in an increasingly interconnected digital environment.
Stay informed and proactive in the face of evolving cyber threats. Cybersecurity remains a top priority in safeguarding digital assets and maintaining trust in an increasingly interconnected world.
Beyond the Headlines: The True Cost of Cybercrime
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has hyper-accelerated the amount of data being generated. This growth will continue exponentially as newer platforms and tools are developed. As businesses turn to novel insurance models, which by definition are new and do not resemble what we have known or used previously to evaluate the risks related to retaining sensitive data in the current cybersecurity climate. Organizations need to understand their risk profile and the financial reality of the loss of access to their data.
it’s more important than ever to truly understand and plan for the threat landscape and the potential financial implications associated with cyber incidents, data exfiltration, and work stoppages.
The importance of data and an organization's capacity to appropriately protect it will be essential factors in assessing overall risk, influencing investors, insurability, and overall profitability.
Ransomware - SMEs Faces Greatest Risk - Attacks Grown 235%
Enterprises, beware. Threat actors are continuing to eye businesses for high returns on investment in Q1 2019, breaching infrastructure, exfiltrating or holding data hostage, and abusing weak credentials for continued, targeted monitoring. From a steadfast increase of pervasive Trojans, such as Emotet, to a resurgence of ransomware lodged against corporate targets, cybercriminals are going after organizations with a vengeance.
Ransomware attacks on business targets have seen a substantial increase in the first quarter of 2019, up by 195 percent since the fourth quarter of 2018, according to a recent Malwarebytes report.
Malwarebytes researchers analyzed the combined statistics and intel collected from its intelligence, research, and data science teams between January 1 and March 31, 2019. They also leveraged telemetry from both consumer and business products on PC, Mac, and mobile devices.
Overall, they found that business detection of ransomware attacks increased by more than 500 percent from the same time frame in 2018 with 336,634 detections.
SMEs face the greatest risk from attacks as overall business detections have grown 235%
“Zero day attacks are on the rise and estimated to be a daily occurrence by 2021. This is largely down to digitisation within organisations and there’s more pressure on developers to deliver software faster – leaving systems vulnerable. This problem is exacerbated by hackers becoming more sophisticated, enabling them to bypass defences more easily.
“IT teams often prioritise stopping a breach occurring at all, but in today’s cyber climate a successful breach is inevitable. The most important aspect of cyber security is that businesses prepare for the worst and have effective data recovery and backup systems in place. Zero day recovery makes sure critical systems are down for as little time as possible. It’s often true that real damage from these breaches doesn’t come from the attack itself, but the resultant downtime after a breach – the time taken to become fully operational dictates the financial and operational fallout on a business.”
Key takeaways
cryptomining seems to have gone the way of the dodo. Detections of consumer-focused Bitcoin miners have dropped significantly over the last year and even from last quarter, while business-focused miners have increased from the previous quarter, especially in the APAC region.
Adware in Macs and mobile devices was problematic.
While all Mac malware saw a more than 60 percent increase from Q4 2018 to Q1 2019, adware was particularly pervasive, clocking in at over 200 percent from the previous quarter. Mobile adware detections also trended upward, as supply chain attacks delivered malware pre-installed on mobile devices. However, overall adware detections were fewer in Q1 2019 than they were during the same time period last year.
Exploit authors developed some attention-grabbing techniques. A new Flash Player zero-day was discovered in Q1 and quickly implemented into popular exploit kits, including Underminer and Fallout EK, as well as a new exploit kit called Spelevor. In addition, a Chrome zeroday required users to take action, fully shutting down and restarting their browser in order to patch the vulnerability. Finally, the popular software WinRAR was being used to deliver payloads to users.
As attacks against businesses ramped up, user trust in businesses to protect their data reached a new low.
In a survey conducted by Malwarebytes in Q1 2019 of nearly 4,000 respondents, users expressed deep concerns about abuse, misuse, and theft of PII, especially from social media and search engine companies. In a new section of our Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques report, we examine how cybercriminals found success by exploiting infrastructure weaknesses, gaps in policy and regulation, and even corporate negligence to not only walk away with valuable data, but establish persistence within the network.
Businesses are still the prime target. Overall detections of threats to businesses have steadily risen, while consumer threats have dropped off. Business detections increased by about 7 percent from the previous quarter, while consumer detections declined by nearly 40 percent, resulting in an overall dip in malware volume of 35 percent quarter over quarter. Compared to Q1 2018, business detections have skyrocketed 235 percent, with consumer detections dropping 24 percent year over year. This reinforces the observed trend of cybercriminals focusing more on business targets today.
Emotet shows no signs of stopping. Emotet, the most fearsome and dangerous threat to businesses today, has made a total shift away from consumers, reinforcing the intent of its creators to focus on enterprise targets, except for a few outlier spikes. Detections of Trojans (Emotet’s parent category) on business endpoints increased more than 200 percent from the previous quarter, and almost 650 percent from the same time last year.
Ransomware is back to business.
Ransomware has made a tremendous comeback against business targets in Q1 2019, with an increase of 195 percent in detections from Q4 2018 to Q1 2019. In comparison to the same time last year, business detections of ransomware have seen an uptick of over 500 percent, thanks in large part to a massive attack by the Troldesh ransomware against US organizations in early Q1.
Consumer detections of ransomware died down. Meanwhile, ransomware consumer detections have continued to drop, despite activity by families such as GandCrab, which primarily targeted consumers over the last quarter as it switched to a ransomware-asa-service and began brute-forcing RDP to infiltrate systems. Consumer detections of ransomware decreased by 10 percent quarter over quarter, and by 33 percent year over year.
What is Cybersecurity Risk Management
Cyber Risk Management is the next evolution in enterprise technology risk and security for organizations that increasingly rely on digital processes to run their business. Risk management is a concept that has been around as long as companies have had assets to protect. The simplest example may be insurance. Life, health, auto and other insurance are all designed to help a person protect against losses. Risk management also extends to physical devices, such doors and locks to protect homes and autos, vaults to protect money and precious jewels, and police, fire and security to protect against other physical risks.
What is cybersecurity risk management?
Rather than doors, locks and vaults, IT departments rely on a combination of strategies, technologies and user education to protect an enterprise against cybersecurity attacks that can compromise systems, steal data and other valuable company information, and damage an enterprise’s reputation. As the volume and severity of cyber attacks grow, the need for cybersecurity risk management grows with it.
Cybersecurity risk management takes the idea of real world risk management and applies it to the cyber world. It involves identifying your risks and vulnerabilities and applying administrative actions and comprehensive solutions to make sure your organization is adequately protected.
Setting up your risk management system
Before setting up a cybersecurity risk management system, the enterprise needs to determine what assets it needs to protect and place a priority on. As the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) points out in its Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, there is no one-size-fits all solution. Different organizations have different technology infrastructures and different potential risks. Some organizations such as financial services firms and healthcare organizations, have regulatory concerns in addition to business concerns that need to be addressed in a cybersecurity risk management system. Cybersecurity should follow a layered approach, with additional protections for the most important assets, such as corporate and customer data. Remember that reputational harm from a breach can do more damage than the breach itself.
Risk management with CyberSecOp
Identity Services
Identity services help companies manage the explosion of digital identities and access to critical resources, both internal and cloud-based. In this age of digital transformation, the spheres of the individual’s life―as a professional, consumer, and private citizen―are interlinked in a complex digital structure, like a piece of fabric. The growing ability to piece together a digital picture of a person’s life and identity carries both risk and opportunity.
Wherever an organization is on its journey, we can help them achieve efficiencies, reduce risk, and evolve to support the changing needs of the digital business. With 20 years of identity management experience across the major industries, we offer field-tested accelerators and methods that are scalable and adaptive to each client’s specific set of business requirements.
Data Protection
Data Protection services help implement capabilities and technologies to protect sensitive data. As infrastructure and applications become more virtualized and adaptive, new cybersecurity gaps can be created as fast as old ones have been addressed, making the prevention of data breaches more difficult than ever. By prioritizing preventative and detective defenses around highly sensitive data, security teams can help reduce data loss and risk when attackers get past network, application, and infrastructure controls.
Leveraging these principles and an understanding of each client’s risk profile, CyberSecOp helps organizations design, implement, and manage capabilities to help better protect sensitive information across the end-to-end data lifecycle, and at an organization’s last line of defense.Application Security
In the era of digital transformation, application portfolios are becoming exponentially more diverse—and support a growing community of users. As the application “surface area” expands, so does cyber risk. Amid the change, one thing remains constant: applications are the lifeline of the business—and need to be a front line of cyber defense. It’s an important time for organizations to reexamine their approaches to application security.
Improving application security requires technical attention to individual applications, but also a broad framework across the application portfolio—from custom-developed to commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) applications and whether managed on-premise, on a mobile platform, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment. It also requires the flexibility to support varying and often coexisting system methodology processes from waterfall, to agile, to DevOps in order to address application-related cyber risk at the pace of the organization’s digital evolution.
CyberSecOp’s application security services help organizations to design and implement security mechanisms across the system development methodology that can flex to your operational requirements to drive value through IT while also protecting your application portfolio against the changing cyber threat landscape.Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure Security services focus on developing advanced protection of core systems and devices. Today’s critical business drivers—the need to digitally transform, modernize the supply chain, enhance customer experience, increase agility, reduce costs, etc.—are driving a major shift in technology priorities. This shift includes increasing focus on cloud adoption, the Internet of Things (IoT), hybrid computing, software-defined networks (SDN), robotic process automation (RPA), blockchain, artificial intelligence, and more. The infrastructure supporting it has become highly virtualized and automated—and the traditional means of securing infrastructure fall short.
CyberSecOp helps organizations move toward a modernized, risk-focused agile defense approach. While the basic infrastructure domains—physical facilities, networks, systems and storage, and endpoints—that need to be protected remain the same, the means to secure them must evolve. By providing assessment, strategy, architecture, implementation, and operational management assistance across the four infrastructure domains, we help clients face our brave new world with a transformed, agile defense capability.
Are Users Your Weakest Link - To Your Cybersecurity Posture
Humans remain the weak link in corporate data protection
Humans remain the weak link in corporate data protection, but you might be surprised that it isn't only rank-and-file employees duped by phishing scams who pose risks. Some companies are lulled into a false sense of cybersecurity by vendors. You read that right, Some enterprises believe the shiny new technologies they've acquired will protect them from anything.
As we continue to build defense in depth and deploy security appliances utilizing AI and other emerging technologies, attackers will continue to pivot to the perennial weak spot: the users. Recently I hosted the Social Engineering Capture The Flag competition at Hackfest in Quebec, and similar to last year, the results were sobering. Every single targeted company had employees that gave detailed information over the phone on their OS and service pack level, and 88 percent gave detailed information on the browser they were using. Three quarters went to a URL that they were given over the phone. The information that the companies bled was disheartening but not shocking. Until we train employees to trust their instincts and tell them it's okay to say no to a customer, things won't change. In the current environment where companies ask their customers to leave a positive review online, employees increasingly feel less empowered to terminate a call they feel is suspicious. Your friendly neighborhood hacker is happy to exploit this weakness.
Billions being send on security tools
The threat of cyber crime has created a significant increase in interest on the topic of cyber security, with organizations spending billions of dollars to protect themselves against a fast evolving array of current and potential future threats. Many spend heavily on monitoring, surveillance and software; however, they often neglect the risk exposure created by their own people – and, in this digital age, by their customers.
Businesses are losing the fight, pay ransom, or lose their lively hood
Businesses are forced to make exceedingly difficult decisions. On one hand, it feels wrong to negotiate with the cybercriminals and give them what they want. On the other hand, the looming financial hit and business interruption is typically far more detrimental than the payoff amount. If business owners don’t engage with the ransomers, they face the prospect that they, and their employees, may lose their livelihood. I see ransomware as a continuing cyber threat in 2019 and beyond. It’s up to business owners to implement the best security practices and ensure that their employees are properly trained to identify and avoid potential threats.
Choosing A Managed Detection & Response Provider
Why Managed Detection & Response Provider may be the right move
Companies outsourcing security need Managed Detection & Response providers (MDR) more than ever to improve cyber resilience. With the security landscape growing more complex, and the costs of maintaining adequate in-house security teams high, it makes sense for many companies to outsource the tasks of threat hunting and response to ensure that they can promptly identify potential threats and react swiftly to mitigate damages. Managed Detection & Response providers often integrate tools such as Endpoint Detection & Response and other solutions to detect threats, analyze risk, and correlate threat data to pinpoint patterns that could indicate a larger attack.
How to choose the right Manged Detection & Response Provider
Smart moves: you’re making them. How do we know? For one, you’re investigating ways to close the gaps in your threat detection and incident response. Which makes sense, given that assembling the talent and tech to thoroughly thwart attackers requires more than most organizations can commit to. Even smarter, you’re checking out Managed Detection and Response (MDR) Services, an increasingly popular solution which combines expertise and tools to provide monitoring and alerting, as well as remote incident investigation and response that can help you detect and remediate threats.
9 things to look our for when choosing a Managed Detection & Response Provider
Your Managed Detection & Response Provider should combine numerous data inputs from security detection tools, threat intel feeds, third party data sources, and the IT asset database to identify not only where there is a threat but its risk compared to others in the queue.
Assess your company's present and future technology needs and initiatives. Qualify, quantify and communicate those needs throughout your company. Is the Managed Detection & Response Provider able to address your range of needs?
Technology strategies should encompass people and processes as part of the organization's mission and strategies. Do they offer ongoing employee training as part of their service?
Does the Managed Detection & Response Provider continuously assess your organization's performance for meeting objectives? You want a partner that focuses on continuous evaluation and improvement of your objectives.
Review your company's goals and mission. Ensure they are clear and concise and can be communicated to all organizational stakeholders as well as your new IT partner.
Perform annual policy and process reviews to assess organization's readiness for external reviews and incident response.
Identify and create teams within your organization to define current challenges and align initiatives to those challenges.
Through playbooks and pre-defined workflows, you can quickly assess and begin to remediate security incidents based on best practices. Ask a Managed Detection & Response Provider if they include such materials as part of their package.
CIOs/CISOs should have unprecedented transparency to all aspects of the security environment. Through dashboards and visualization techniques, CIOs/CISOs will be more easily able to communicate with Managed Detection & Response Providers which vulnerabilities and threats exist and the risks of inaction.
CEOs and Cyber Security: are they the road block?
CEOs and cybersecurity: are they the road block?
Senior executives may be the weakest link in the corporate cyber security chain and are a primary target of hackers, fraud and phishing scams, says report. it also should be know that the are the road block to approve budget for information security, and most often security takes back sit to profit.
Report by many source and research done by many firm identity senior executive has the road block to good security within their firms, Many CEOs think they are immune to hackers, at least that’s what a new report According to the report, these findings are ironic given that CEOs are the ideal victim.
Senior Executive Are You the Weakest Link?
According to the report, Are You the Weakest Link? How Senior Executives Can Avoid Breaking the Cybersecurity Chain, many senior executives ignore the threat from hackers and cyber criminals and often feel that security policies in their respective organisations do not apply to their unique position.
In reality, their often privileged access to company information makes their personal accounts extremely valuable to exploit and heightens the need for extra care.
Professional hackers and adversaries will usually do a thorough investigation into a senior executive or board level director, including full analysis which could entail in-depth monitoring of the company website and associated social media accounts (including employees and their extended networks).
It appears that many CEOs commonly view cyber security as a responsibility for the IT department only. In reality, IT security has now become a remit for all individuals.
“All employees — especially those at the top of the corporate ladder — need to realise that cybercriminals use social engineering, email phishing and malware to access personal accounts, and C-level staff especially need to avoid becoming the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain by adhering to regularly updated, company-wide security policies regarding data sharing and backup,”
“Reviewing corporate policies, with a focus on people, premises, processes, systems and suppliers will provide valuable insights into which areas to improve, and by championing a ‘security first’ corporate culture, organisations and their senior executives will be well positioned to avoid the high financial costs, reputation damage and unexpected downtime that could result from a cyberattack or data breach.”
Cyber Security Do's and Don'ts
Information and Cyber Security Consulting Services: Cyber security systems and principles are designed to safeguard company data, websites and web applications from attackers seeking to disrupt, delay, alter or redirect the flow of data. These attackers vary in target, motive, levels of organization, and technical capabilities, requiring public and private organizations to adopt ever-increasing measures to prevent cyber attacks. CyberSecOp is an award winning US based to Cyber Security Consulting Company.
The following are some important do’s and don’ts for advisers to keep in mind when executing on the action steps in your cybersecurity plan:
Make use of all tools available from your broker-dealer or custodian. The securities industry is investing tens of millions of dollars in cybersecurity, making tools and resources available to advisers and their teams. Actively seek out those tools and become known at your firm for your interest in and commitment to cybersecurity.
Eliminate weak links in your system. Hackers will be turned away from your systems that use strong passwords and encryption. Don’t let users share passwords. In addition to PCs, encrypt
all thumb drives, cell phones and tablets. And set untended computers to lock automatically after a set number of minutes.
Take preparation, training and review seriously. Put effort into your plan, review it seriously on a regular basis, document that review, and make sure that all staff – including even those who don’t usually deal with clients or their information – are regularly trained and updated on cybersecurity policies and procedures. Since staff carelessness or inattention can be the weakest link
in the defense chain, make sure that you and your staff never download an attachment or accept a request if it can’t be verified.
Be alert to things that don’t feel right. Suppose, for example, that a staff member receives a phone call from someone saying he’s from Microsoft tech support and has noticed a computer virus on your system. Even if the employee isn’t aware that reputable tech support operations don’t work that way, he or she should immediately sense that the call is out of the ordinary and somehow amiss. Given that feeling, the employee should hang up immediately and not let the unidentified caller connect to the firm’s system. Similarly, if you or staff receive an e-mail from a client saying they’ve been mugged on vacation or have lost their wallet or passport, most likely their e-mail has been hacked. Contact that person via landline or cell phone and confirm the story.
Educate your users and clients in how to communicate safely. Advisers should require multifactor authentication (use of a token or other identifier beyond password or ID) for client communication through Gmail, Yahoo! and other major providers. This will protect them, and you, from hackers.
Don’t keep cybersecurity a secret. The financial advice business is competitive, but there is one area where cooperation, not competition, is paramount: cybersecurity. Discuss the issue frequently with peers and share any ideas you have.
Don’t lull yourself into thinking cybersecurity is someone else’s problem. Be alert to news and developments in cybercrime and cybersecurity and seek more information and update plans and programs accordingly. Start by identifying your three biggest potential threats and get to work addressing them.
Ransomware Cyberattack - 92% of MSSPs Expect Ongoing Attacks
Ransomware is the leading cyberattack experienced by small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), according to a survey of more than 2,400 managed service providers (MSSPs) conducted by data protection company Datto.
Datto’s State of the Channel Ransomware Report provides unique visibility into the ransomware epidemic from the perspective of the IT Channel and the SMB clients who are dealing with these infections on a daily basis. The report provides a wealth of detail on ransomware, including year-over-year trends, frequency, targets, impact, and recommendations for ensuring recovery and continuity in the face of the growing threat.
Key findings from Datto’s “State of the Channel Ransomware Report” included:
79 percent of MSSPs reported ransomware attacks against customers.
85 percent indicated that victims had antivirus software installed, 65 percent reported victims had email/spam filters installed and 29 percent reported victims used pop-up blockers.
89 percent are “highly concerned” about ransomware attacks.
92 percent predict the number of ransomware attacks will continue at current, or worse, rates.
MSPs ranked phishing emails as the top ransomware delivery method, followed by malicious websites, web ads and clickbait.
The average requested ransom for SMBs is roughly $4,300, while the average cost of downtime related to such an attack is approximately $46,800.
The number of MSPs reporting OS/iOS attacks increased by nearly 500 percent year over year in the first six months of 2018.
No single solution is guaranteed to prevent such attacks, Datto indicated. Conversely, SMBs require a multilayered approach to identify and stop ransomware attacks before they cause brand reputation damage, revenue loss and other problems.
How Can SMBs Address Ransomware Attacks?
CyberSecop offered the following recommendations to help SMBs safeguard their data and assets against such attacks:
Leverage business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) technology. BCDR technology won’t stop ransomware attacks; instead, it helps an SMB determine how to limit downtime and maintain operations despite a ransomware attack.
Provide cybersecurity training. By offering regular and mandatory cybersecurity training, an SMB can ensure all of its employees can identify and avoid potential phishing scams that otherwise lead to such an attack.
Employ a dedicated cybersecurity professional. It may be difficult for an SMB to hire a full-time cybersecurity professional. Fortunately, working with an MSSP allows an SMB to receive cybersecurity monitoring and other security services.
Cyber Insurance - Is a must have - you will need it
Cyber Insurance - Is a must have - you will need it.
It’s every healthcare organization’s nightmare to get the call that their data has been breached or hacked. As a result, many have turned to cyber insurance to protect assets and business operations.
As cyber policies and carriers lack a universal policy, there’s an even greater worst case scenario: An organization is breached, and the policy doesn’t cover what the leaders thought it did. Now, not only is the healthcare provider strapped with the burden of the breach, it wasted money on a useless cyber insurance policy.
To get a better grasp on how to choose the right policy, Healthcare IT News asked attorney Matthew Fisher, partner with Mirick O’Connell, and Jane Harper, Henry Ford Health System’s director of privacy and security risk management, to outline the biggest policy mistakes -- and how to avoid them.
Mistake #1: Rushing the process
When buying a policy, a carrier will provide a questionnaire that will evaluate your organization’s security posture, program, tools and policies. The biggest mistake is to rush the pre-policy process to see the rates and what the carrier will cover, explained Fisher.
Organizations need to be conservative with how they answer the questions, as “it could be a ground for denial, if you don’t have the policies you said you have in place,” said Fisher. “You have to make sure you’re not unintentionally misleading the insurance company when it comes to coverage.”
Often these questionnaires attempt to create a black and white policy and “it can be tough to answer correctly,” explained Fisher.
“Your ability to be as transparent and truthful upfront is critical to the nonpayment discussion,” said Harper. “If you tell the insurance company that you have everything in place and are compliant, if you tell them that and then you have an issue, and you weren’t truthful, it ends up being a legal battle.”
“When you submit your checklist that they have you fill out, meet with the underwriter to make sure you understand what you’ve documented,” she added. “You also need the copy that was provided to the insurance company because it will come back into play when you submit the final documents.”
For example, if you say you have a specific control in place, and you actually don’t, Harper explained that can create a situation where “they thought they had an understanding of something, but they didn’t.”
“Be honest, transparent and accurate -- because they can deny your policy if you were inaccurate or misleading in your responses,” she said.
Mistake #2: Lax, incomplete risk assessment
It’s easier to prevent a misleading or false statement to an underwriter, when an organization has a strong assessment and inventory of the processes and tools on the system. But far too often, hospitals “don’t know everything about the control environment,” explained Harper.
“When you talk about protecting an system and preventing a cyber incident, you have to have a good understanding of the organization’s overall control environment,” Harper said. “It’s key, as the longer it takes you to identify that you’ve had an incident, it leads to more exposure and the longer it takes to recover.”
But it’s also important to remember to update this inventory or assessment when buying new tools, merging with other organizations, hiring new staff and the like, Harper explained.
“Think about all of the activities and operations that happen,” she said. “And every three years, you’re updating a cybersecurity checklist -- that may not be frequent enough.”
For example, Harper explained that an organization filling out the policy questionnaire may have all of the right elements in place. But if another tool was purchased and the controls weren’t updated or the control was removed and the underwriter was not notified, there could be a problem.
“If those controls played into how the underwriter rated you: that can be key,” said Harper. “Think about your own home: you get additional discounts when you have a burglar alarm. So if you get one, and let them know, you may get a lower rate… But if you no longer have that control, you have to tell the carrier.”
“It’s the same kind of practice that we want to get into when we get into cyber insurance for our organization,” she added.
Mistake #3: Failing to involve the right people
Many organizations understand that security needs to exist outside of the IT team. In the same vein, it’s crucial when buying a cyber insurance policy that the same mentality is applied to make sure all of your bases are covered.
“Make sure you are talking to the right individuals,” Harper said. “The appropriate key stakeholders are not only involved with the evaluation process - how many patients, how much data, etc. -- but also the responses to the questions the policy is going to ask.”
“Risk folks typically talk about it as it relates to patients,” she continued. “Those folks are key, but in addition, you need your privacy and security risk professionals, security officers, IT leader, your key business leaders/owners and those driving the data. It’s key.”
Also crucial? Making sure the facilities team is involved, as there can sometimes be a cyber incident based on a physical issue. Harper explained that “often people tend to focus on things like electronic PHI, but there’s physical PHI. If there’s a break in at a warehouse and data is stolen, OCR considers that a breach.”
Mistake #4: Failing to understand coverage
Far too often organizations make large assumptions as to just what cyber insurance will cover. Fisher explained that these leaders are often shocked to learn that they did not receive the full spectrum of coverage they wanted.
“Relying on blind faith on those terms, or what the broker or agent is telling you is a major mistake,” said Fisher. “It’s always up to up to you to go into something with eyes fully wide open to make sure you know what you’re actually buying.”
Harper took it a step further and laid to rest a common misconception when it comes to coverage: “Insurance will not cover fines and penalties associated with noncompliance. If you’re not complaint, and you didn’t do risk assessments, cyber insurance won’t protect you from that, so don’t expect it.”
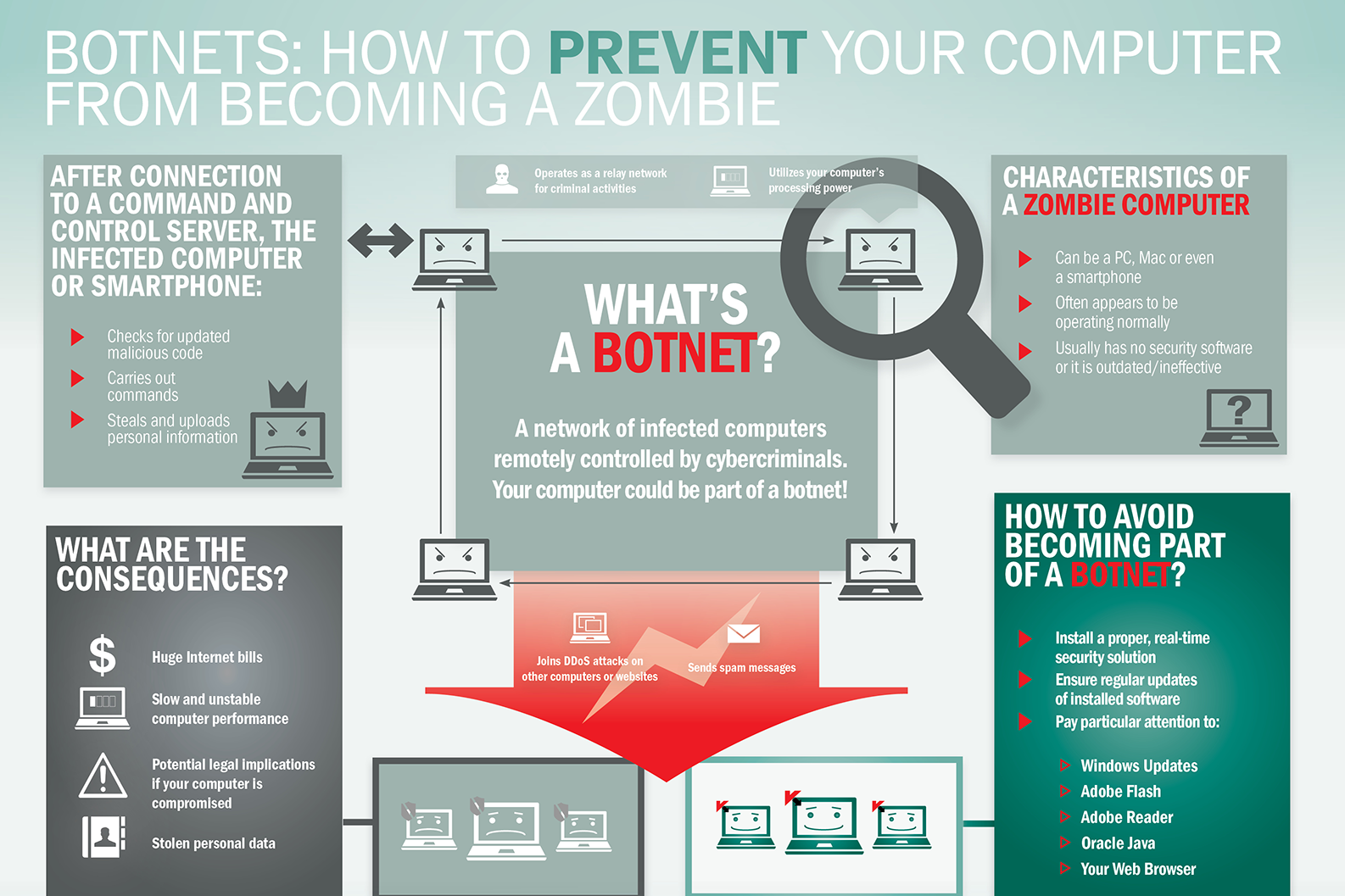
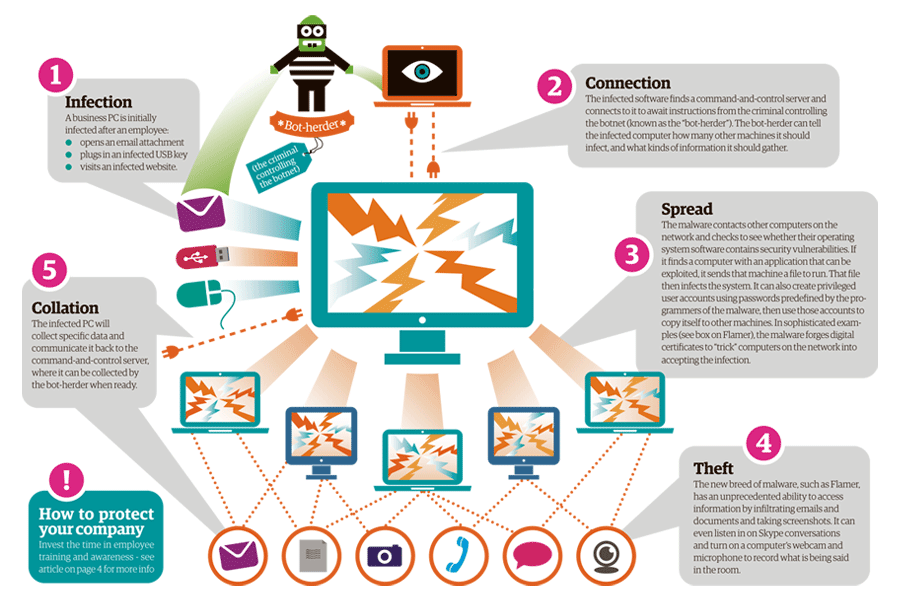
What is Botnet - Cybercriminals #1 Weapon
The word Botnet is formed from the words ‘robot’ and ‘network’. Cybercriminals use special Trojan viruses to breach the security of several users’ computers, take control of each computer and organise all of the infected machines into a network of ‘bots’ that the criminal can remotely manage.
Botnet Prevention- What is Botnet
How Botnets can impact you
Often, the cybercriminal will seek to infect and control thousands, tens of thousands or even millions of computers – so that the cybercriminal can act as the master of a large ‘zombie network’ – or ‘bot-network’ – that is capable of delivering a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, a large-scale spam campaign or other types of cyberattack.
In some cases, cybercriminals will establish a large network of zombie machines and then sell access to the zombie network to other criminals – either on a rental basis or as an outright sale. Spammers may rent or buy a network in order to operate a large-scale spam campaign.
How to prevent your computer becoming part of a Botnet
Installing effective anti-malware software will help to protect your computer against Trojans and other threats.
Small Business Benefits from Cybersecurity Consulting Services
Cybersecurity news stories are becoming more and more prevalent, especially over the last few years. Whether the stories are about stolen emails or huge data breaches, it has been virtually impossible to ignore them.
While the major stories about compromised corporations and hacked email accounts make the news, cybersecurity is something that concerns everyone who uses a computer. Even small business owners can become victims of cybercrime. In fact, small business owners, in particular, need to be concerned with cybersecurity so they can protect their intellectual property. No matter whether the intellectual property is research or recipes, it is one of the greatest assets a small business has. Intellectual property is a prime target for hackers, whether they are stealing information for a competitor or running a ransomware scheme where a hacker demands something in return for the stolen information.
The trouble is that protecting that intellectual property and keeping other sensitive information, such as client and customer data, isn’t cheap. Many small business owners may not have the available capital to afford a cybersecurity system. Although this puts an owner in a tough spot, you can’t put a price on peace of mind, and neither can a small business owner afford the losses associated with becoming the victim of a cybercrime.
As with most things for small-business owners, cybersecurity comes down to a cost analysis. A cybersecurity system can be a big expense. On the other hand, a small business owner has to consider the cost of not having their systems protected from hackers. It’s hard enough for a large corporation to recover from a cyber attack, even with all the resources and infrastructure they have. According to the U.S. National Cyber Security Alliance, 60 percent of small businesses fold within six months of a cyber attack.
Ultimately, each business owner has to decide if and when a formal data security protection plan is necessary. A consultation with an expert may help you better weigh the pros and cons of taking on this type of business expense. Start with this list of Cybersecurity Consulting Providers as a jumping off point for your research. After comparing the benefits of these companies’ plans, set up a few consultations to see if and how these providers can best help protect your business, and what it costs to do so. You may find that it’s worth the investment.