CYBER SECURITY CONSULTING SERVICE AWARDS AND RECOGNITIONS
CyberSecOp's comprehensive managed security services, cyber security consulting, professional services, and data protection technology are recognized as industry-leading threat detection and response solutions by major analyst firms, key media outlets, and others.
MSSP Cybersecurity & Managed Detection and Response
MSSP Cybersecurity & Managed Detection and Response
Managed detection and response enables a proactive approach to security with its ability to detect and fully analyze threats and promptly respond to incidents. CyberSecOp Threat intelligence is one of the key aspects our security consultants used to help organizations make decisions on how to combat threats. Through managed detection and response, organizations can take advantage of the threat intelligence capabilities of security experts.
How Managed Detection and Response Provides Effective Threat Intelligence
Capture full visibility across your entire IT environment
Detect the most advanced threats (known and unknown) designed to bypass your traditional perimeter security controls, even when no malware is used
Expose threat actors currently hiding in your environment
Gain 24x7 monitoring by an advanced team of security experts that are specially trained to analyze advanced threats, determine the severity of any incidents and provide actionable guidance to remediate
Quickly elevate the alerts that matter most so you can focus limited resources where it matters most
Managed Detection and Response Service
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is an all-encompassing cybersecurity service used to detect and respond to cyber-attacks. Using the best of signature, behavioral and anomaly detection capabilities, along with forensic investigation tools and threat intelligence, human analysts hunt, investigate and respond to known and unknown cyber threats in real time 24x7x365. Get Managed Detection and Response Services for your business www.cybersecop.com.
Ransomware Cyberattack - 92% of MSSPs Expect Ongoing Attacks
Ransomware is the leading cyberattack experienced by small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), according to a survey of more than 2,400 managed service providers (MSSPs) conducted by data protection company Datto.
Datto’s State of the Channel Ransomware Report provides unique visibility into the ransomware epidemic from the perspective of the IT Channel and the SMB clients who are dealing with these infections on a daily basis. The report provides a wealth of detail on ransomware, including year-over-year trends, frequency, targets, impact, and recommendations for ensuring recovery and continuity in the face of the growing threat.
Key findings from Datto’s “State of the Channel Ransomware Report” included:
79 percent of MSSPs reported ransomware attacks against customers.
85 percent indicated that victims had antivirus software installed, 65 percent reported victims had email/spam filters installed and 29 percent reported victims used pop-up blockers.
89 percent are “highly concerned” about ransomware attacks.
92 percent predict the number of ransomware attacks will continue at current, or worse, rates.
MSPs ranked phishing emails as the top ransomware delivery method, followed by malicious websites, web ads and clickbait.
The average requested ransom for SMBs is roughly $4,300, while the average cost of downtime related to such an attack is approximately $46,800.
The number of MSPs reporting OS/iOS attacks increased by nearly 500 percent year over year in the first six months of 2018.
No single solution is guaranteed to prevent such attacks, Datto indicated. Conversely, SMBs require a multilayered approach to identify and stop ransomware attacks before they cause brand reputation damage, revenue loss and other problems.
How Can SMBs Address Ransomware Attacks?
CyberSecop offered the following recommendations to help SMBs safeguard their data and assets against such attacks:
Leverage business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) technology. BCDR technology won’t stop ransomware attacks; instead, it helps an SMB determine how to limit downtime and maintain operations despite a ransomware attack.
Provide cybersecurity training. By offering regular and mandatory cybersecurity training, an SMB can ensure all of its employees can identify and avoid potential phishing scams that otherwise lead to such an attack.
Employ a dedicated cybersecurity professional. It may be difficult for an SMB to hire a full-time cybersecurity professional. Fortunately, working with an MSSP allows an SMB to receive cybersecurity monitoring and other security services.
Data Breaches Ransomware and Cyber Attacks
Data Breaches Ransomware and Cyber Attacks
It’s unrealistic to think that you can completely avoid cyberattacks and data breaches, so it’s vital to have a proper data recovery plan in place. You can also tighten your defenses significantly by ensuring all of your network devices are properly configured, and by putting some thought into all of your potential network borders.
Data Recovery Capability
Do you have a proper backup plan in place? Have you ever tested it to see that it works? Disaster recovery is absolutely vital, but an alarming number of companies do not have an adequate system in place. A survey of 400 IT executives by IDG Research revealed that 40% rate their organizations’ ability to recover their operations in the event of disaster or disruption as “fair or poor.” Three out of four companies fail from a disaster recovery standpoint, according to the Disaster Recovery Preparedness Benchmark.
A successful malware attack can lead to altered data on all compromised machines and the full effects are often very difficult to determine. The option to roll back to a backup that predates the infection is vital. Backed up data must be encrypted and physically protected. It’s also important that a test team routinely checks a random sampling of system backups by restoring them and verifying data integrity.
Secure Configurations for Network Devices such as Firewalls, Routers, and Switches
The default configurations for network devices like firewalls, routers, and switches are all about ease of use and deployment. They aren’t designed with security in mind and they can be exploited by determined attackers. There’s also a risk that companies will create exceptions for business reasons and then fail to properly analyze the potential impact.
The 2015 Information Security Breaches Survey found that failure to keep technical configuration up to date was a factor in 19% of incidents. Attackers are skilled at seeking out vulnerable default settings and exploiting them. Organizations should have standardized secure configuration guidelines applied across devices. Security updates must be applied in a timely fashion.
You need to employ two-factor authentication and encrypted sessions when managing network devices, and engineers should use an isolated, dedicated machine without Internet access. It’s also important to use automated tools to monitor the network and track device configurations. Changes should be flagged and rule sets analyzed to ensure consistency.
Boundary Defense
When the French built the Maginot Line in World War II, a series of impregnable fortifications that extended along the border with Germany and beyond, it failed to protect them because the Germans invaded around the North end through neutral Belgium. There’s an important lesson there for security professionals: Attackers will often find weaknesses in perimeter systems and then pivot to get deeper into your territory.
They may gain access through a trusted partner, or possibly an extranet, while your defensive eye is focused on the Internet. Effective defenses are multi-layered systems of firewalls, proxies, and DMZ perimeter networks. You need to filter inbound and outbound traffic and take caution not to blur the boundaries between internal and external networks. Consider network-based IDS sensors and IPS devices to detect attacks and block bad traffic.
Segment your network and protect each sector with a proxy and firewall to limit access as far as possible. If you don’t have internal network protection, then intruders can get their hands on the keys to the kingdom by successfully breaching the outer defenses.
The real cost
A lot of businesses argue that they can’t afford a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, but they should really consider whether they can afford to lose all their data or be uncertain about its integrity. They may lack the expertise to ensure that network devices are securely configured, but attackers don’t lack the skills to exploit that. It’s understandably common to focus on the outer boundary of your network and forget about threats that come from unexpected directions or multiply internally, but it could prove costly indeed.
Compared to the cost of a data breach, all of these things are cheap and easy to set up
Ransomware Business Impacts, Ransomware Business Cost
Projecting the overall cost of a ransomware attack can be tricky for security executives considering the many factors that can come into play when responding to and recovering from one. Information from numerous previous incidents show the costs go well beyond any demanded ransom amount and the costs associated with cleaning infected systems.
Ransomware is defined as a form of malicious software that is designed to restrict users from accessing their computers or files stored on computers till they pay a ransom to cybercriminals. Ransomware typically operates via the crypto virology mechanism, using symmetric as well as asymmetric encryption to prevent users from performing managed file transfer or accessing particular files or directories. Cybercriminals use ransomware to lock files from being used assuming that those files have extremely crucial information stored in them and the users are compelled to pay the ransom in order to regain access.
Ransomware History
It’s been said that Ransomware was introduced as an AIDS Trojan in 1989 when Harvard-educated biologist Joseph L. Popp sent 20,000 compromised diskettes named “AIDS Information – Introductory Diskettes” to attendees of the internal AIDS conference organized by the World Health Organization. The Trojan worked by encrypting the file names on the customers’ computer and hiding directories. The victims were asked to pay $189 to PC Cyborg Corp. at a mailbox in Panama.
From 2006 and on, cybercriminals have become more active and started using asymmetric RSA encryption. They launched the Archiveus Trojan that encrypted the files of the My Documents directory. Victims were promised access to the 30-digit password only if they decided to purchase from an online pharmacy.
After 2012, ransomware started spreading worldwide, infecting systems and transforming into more sophisticated forms to promote easier attack delivery as the years rolled by. In Q3, about 60,000 new ransomware was discovered, which doubled to over 200,000 in Q3 of 2012.
The first version of CryptoLocker appeared in September 2013 and the first copycat software called Locker was introduced in December of that year.
Ransomware has been creatively defined by the U.S. Department of Justice as a new model of cybercrime with a potential to cause impacts on a global scale. Stats indicate that the use of ransomware is on a steady rise and according to Veeam, businesses had to pay $11.7 on average in 2017 due to ransomware attacks. Alarmingly, the annual ransomware-induced costs, including the ransom and the damages caused by ransomware attacks, are most likely to shoot beyond $11.5 billion by 2019.
Ransomware Business Impacts Can Be Worrisome
Ransomware can cause tremendous impacts that can disrupt business operations and lead to data loss. The impacts of ransomware attacks include:
Loss or destruction of crucial information
Business downtime
Productivity loss
Business disruption in the post-attack period
Damage of hostage systems, data, and files
Loss of reputation of the victimized company
You will be surprised to know that apart from the ransom, the cost of downtime due to restricted system access can bring major consequences. As a matter of fact, losses due to downtime may cost tens of thousands of dollars daily.
As ransomware continues to become more and more widespread, companies will need to revise their annual cybersecurity goals and focus on the appropriate implementation of ransomware resilience and recovery plans and commit adequate funds for cybersecurity resources in their IT budgets.
Consider the following examples. The Erie County Medical Center (ECMC) in Buffalo, NY, last July estimated it spent $10 million responding to an attack involving a $30,000 ransom demand. About half the amount went toward IT services, software, and other recovery-related costs. The other half stemmed from staff overtime, costs related to lost revenues, and other indirect costs. ECMC officials estimated the medical center would need to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars more on upgrading technology and employee awareness training.
Public records show that the City of Atlanta spent almost $5 million just in procuring emergency IT services following a March 2018 ransomware attack that crippled essential city services for days. The costs included those associated with third-party incident response services, crisis communication, augmenting support staff and subject matter expert consulting services.
In Colorado, Gov. John Hickenlooper had to set aside $2 million from the state disaster emergency fund after ransomware infected some 2,000 Windows systems at CDOT, the state department of transportation, this February. In less than eight weeks, CDOT officials spent more than half that amount just returning systems to normal from the attack.
Not surprisingly, industry estimates relating to ransomware damages have soared recently. Cybersecurity Ventures, which pegged ransomware costs at $325 million in 2015, last year estimated damages at $5 billion in 2017 and predicted it would exceed $11.5 billion in 2019.
For security executives trying to prepare a total ransomware cost estimate, the key is not to get fixated on the ransom amount itself. Even if you end up paying it to recover your data—something that most security analysts advocate against—the actual costs of the attack in most cases will end up being greater.
Risk Facing Financial Services
Risk Facing Financial Services
Financial services institutions have changed significantly over the last decade – from utilizing technology in new ways to stay competitive and drive efficiencies, to adapting business practices in light of the global financial crisis and recent narrow interest margin markets.
As these businesses evolve, they’re faced with a new range of exposures that can result in significant and lasting commercial costs, and traditional exposures come to light in a different context. Crime has also changed for these businesses, with a growing number of attacks against financial institutions taking place online and through digital means.
To better understand this changing landscape, we’ve outlined the top risks facing financial institutions today:
Social engineering and funds transfer fraud
Some of the most frequent cyber claims made by businesses in the past year involved funds transfer fraud and some form of social engineering. Funds transfer fraud is often carried about by criminals leveraging fraudulent emails or phone calls to request the transfer of funds from a legitimate account to their own. In some cases, fraudsters will pose as a senior executive appearing to give urgent instructions to a junior employee. While financial institutions have greater control processes, including separation of responsibilities, both banks and their clients are at risk of falling victim to these types of attacks, and as long as they continue to prove successful, we expect this threat to grow in both frequency and severity. Financial institutions should consider employee training on these newer forms of fraud, including how to identify phishing emails. Banks should also be concerned about their customers’ susceptibility to social engineering fraud, and should consider education campaigns where relevant.
Adherence to post-crisis regulation
Following the mortgage crisis in 2007-2008 and the subsequent global financial crisis, the regulatory burden for banks has increased significantly. This brings additional costs when meeting these new requirements, along with higher potential penalties if an institution fails to comply. In many instances, resultant fines and penalties following regulatory failures are uninsured or uninsurable. Financial institutions should seek cover where regulatory enquiry costs and expenses are covered.
Falling prey to predatory banking
Financial institutions have found themselves in a narrow interest margin environment, which means the pressure on banks to generate revenue from non-interest earnings is intense. In some cases, the desire to drive revenue through new or existing products has led to instances of selling inappropriate products to consumers, resulting in significant consumer claims. Institutions must ensure that their products are suitable and that they meet the needs of the consumer and the consumer’s expectations. It’s also important for institutions to ensure their remuneration policies do not inadvertently encourage the miss-selling of products. The fallout from consumer protection scandals can be costly not only from a legal and regulatory standpoint, but also in terms of damage to the brand.
Reputational damage
Predatory banking is only one type of behavior that can bring reputational harm to financial institutions. Large institutions can suffer backlash for a variety of misdeeds made public, for instance the failure in anti-money laundering controls by Wells Fargo or HSBC, who were hammered in the media for their behavior. On a smaller scale, for regional and community-based institutions, the power of social media can mean that reputational damage spreads far faster than ever before.
Systemic instability
Nearly a decade later, the effects of the global financial crisis are still being felt by financial institutions around the world. Recent concerns over Deutsche Bank’s operational cut backs and stock price decline have shown there is still uncertainty around the performance of even the biggest financial organizations. Additionally, recent instability in Europe – particularly in Italy and Spain, as well as the still incomplete negotiation – could have effect elsewhere, including the US, where European headquartered institutions such as Deutsche Bank, Barclays and HSBC are systemically significant institutions.
Challenger banks and new technology
The traditional banking model is increasingly challenged by newcomers trying to use technology to replace existing processes and disrupt the status quo. In the UK and Europe, challenger banks are gaining steam and traction among younger generations and early adopters. In the US, there are few online-only challenger banks, but there is increasing competition from payment processors, online non-bank lenders and other providers who are edging their way towards areas conventionally controlled by banks. The risk for traditional institutions will not only be economic, but they will also need to provide more services to their clients to ensure they are competitive and relevant, and they may need to reassess their cyber exposure as they put more systems online.
Cybersecurity Future and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
As businesses struggle to combat increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity attacks, the severity of which is exacerbated by both the vanishing IT perimeters in today’s mobile and IoT era, coupled with an acute shortage of skilled security professionals, IT security teams need both a new approach and powerful new tools to protect data and other high-value assets. Increasingly, they are looking to artificial intelligence (AI) as a key weapon to win the battle against stealthy threats inside their IT infrastructures, according to a new global research study conducted by the Ponemon Institute on behalf of Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company (NYSE:HPE).
The Ponemon Institute study, entitled “Closing the IT Security Gap with Automation & AI in the Era of IoT,” surveyed 4,000 security and IT professionals across the Americas, Europe and Asia to understand what makes security deficiencies so hard to fix, and what types of technologies and processes are needed to stay a step ahead of bad actors within the new threat landscape.
The research revealed that in the quest to protect data and other high-value assets, security systems incorporating machine learning and other AI-based technologies are essential for detecting and stopping attacks that target users and IoT devices. The majority of respondents agree that security products with AI functionality will help to:
Reduce false alerts (68 percent)
Increase their team’s effectiveness (63 percent)
Provide greater investigation efficiencies (60 percent)
Advance their ability to more quickly discover and respond to stealthy attacks that have evaded perimeter defense systems (56 percent)
Twenty-five percent of respondents said they currently use some form of an AI-based security solution, with another 26 percent stating they plan on deploying these types of products within the next 12 months.
Current Security Tools are not Enough
“Despite massive investments in cybersecurity programs, our research found most businesses are still unable to stop advanced, targeted attacks – with 45 percent believing they are not realizing the full value of their defense arsenal, which ranges from 10 to 75 security solutions,” said Larry Ponemon, chairman, Ponemon Institute. “The situation has become a ‘perfect storm,’ with nearly half of respondents saying it’s very difficult to protect complex and dynamically changing attack surfaces, especially given the current lack of security staff with the necessary skills and expertise to battle today’s persistent, sophisticated, highly trained, and well-financed attackers. Against this backdrop, AI-based security tools, which can automate tasks and free up IT personnel to manage other aspects of a security program, were viewed as critical for helping businesses keep up with increasing threat levels.”
IoT and Cloud Adds Significant Risk
Ponemon researchers found that the majority of IT security teams believe that a key gap in their company’s overall security strategy is their inability to identify attacks that use IoT devices as the point of entry. In fact, more than three-quarters of respondents believe their IoT devices are not secure, with 60 percent stating even simple IoT devices pose a threat. Two-thirds of respondents admitted they have little or no ability to protect their “things” from attacks. Continuous monitoring of network traffic, closed-loop detection and response systems, and detecting behavioral anomalies among peer groups of IoT devices, were cited as the most effective approaches to better protect their environments.
Even the ownership model for IoT security presents potential risk. When asked who inside their organization was responsible for IoT security, responses ranged from the CIO, CISO, CTO, and line-of-business leaders, with no majority consensus. Only 33 percent identified the CIO, with no other executive or functional group achieving response totals above 20 percent. Surprisingly, “No Function” was the third-highest answer (15 percent).
Survey results also highlighted the importance of visibility and the ability to define which resources that people and IoT devices can access, with 63 percent of respondents stating network access control is an important element of their company’s overall security strategy and critical for reducing the reach of inside exploits. Also cited as important was having detailed information about applications (71 percent), endpoints (69 percent), cloud (64 percent), and networks (63 percent), with more than half saying they currently deploy network access control solutions for enabling visibility and control across both wired and wireless networks.
Additionally, more than half of respondents said it’s hard to protect expanding and blurring IT perimeters resulting from requirements to concurrently support IoT, BYOD, mobile, and cloud initiatives (55%).
“Partnering with the Ponemon Institute helps us to improve customer experiences by better understanding security teams’ challenges, and then arming them with advanced solutions that enable quick identification and responses to an ever-changing threat landscape,” said Larry Lunetta, vice president of security solutions marketing for Aruba. “The insight gained from this study enables us to continually improve our ability to provide an enterprise wired and wireless network security framework with an integrated and more comprehensive approach for gaining back visibility and control.”
Cyber security IT skills in-demand in US
There’s no doubt that demand for the technologically skilled will only increase in the upcoming years, as practically every company becomes a software-driven enterprise. A survey by the jobs site Monster found that in the US, jobs in the digital sector have multiplied at more than twice the rate of other non-digital tech sectors, and are predicted to grow by 20% in the next decade.
However, which skills will be particularly in demand? While it’s unlikely that the IT skills demanded by the jobs market today will become redundant within our lifetimes, the field is constantly evolving, and there are certainly growth areas on the horizon that IT professionals would do well to educate themselves in.
Cyber security
Cyber security is an area set to grow exponentially in importance in the upcoming years. Every time a breach is suffered by an organisation, there is a huge cost both in terms of financial loss and loss of reputation and brand value.
A recent study carried out by jobs site Indeed indicated that the US is dangerously short on cyber security skills and that the number of cyber security jobs advertised in the US is the third highest globally, meaning demand exceeded candidate interest by more than three times.
Development
Demand for skills in development is here to stay (for the time being anyway – this could change as soon as AI is more widely used to code). In 2017, the demand for software developers and engineers increased by 13% in the UK.
Devops
Another important area of growth is the trend for companies to take a devops approach to their IT departments, meaning that developers well versed in this outlook will be the most employable.
Cloud computing
It’s widely recognised that cloud computing is the future, and every IT professional should feel comfortable using these systems. Demand for cloud infrastructure specialists is increasing across the board.
Machine Learning and AI
These are two obvious areas of increasing growth. In the US, demand for AI jobs increased threefold between 2015 and 2018, even surpassing the UK in terms of demand.
Prevent DDoS attacks across your enterprise
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks feature amongst the most dreaded kinds of cyber attacks, for any enterprise today. This is especially because, as the name itself suggests, there it causes a total denial of service; it exhausts all resources of an enterprise network, application or service and consequently it becomes impossible to gain access to the network, application or the service.
In general, a DDoS attack is launched simultaneously from multiple hosts and it would suffice to host the resources, the network and the internet services of enterprises of any size. Many prominent organizations today encounter DDoS attacks on a daily basis. Today DDoS attacks are becoming more frequent and they are increasing in size, at the same time becoming more sophisticated. In this context, it becomes really important that enterprises look for DDoS attack prevention services, in fact the best DDoS attack prevention services, so as to ensure maximum protection for their network and data.
The different kinds of DDoS attacks
Though there are different kinds of DDoS attacks, broadly speaking there are three categories into which all the different kinds of DDoS attacks would fit.
The first category is the volumetric attacks, which include those attacks that aim at overwhelming network infrastructure with bandwidth-consuming traffic or by deploying resource-sapping requests. The next category, the TCP state-exhaustion attacks, refer to the attacks that help hackers abuse the stateful nature of the TCP protocol to exhaust resources in servers, load balancers and firewalls. The third category of DDoS attacks, the application layer attacks, are basically the ones targeting any one aspect of an application or service at Layer 7.
Of the above-mentioned three categories, volumetric attacks are the most common ones; at the same time there are DDoS attacks that combine all these three vectors and such attacks are becoming commonplace today.
DDoS attacks getting sophisticated, complex and easy-to-use
Cybercriminals today are getting cleverer and smarter. They tend to package complex, sophisticated DDoS attack tools into easy-to-use downloadable programs, thereby making it easy even for non-techies to carry out DDoS attacks against organizations.
What are the main drivers behind DDoS attacks? Well, there could be many, ranging from ideology or politics to vandalism and extortion. DDoS is increasingly becoming a weapon of choice for hacktivists as well as terrorists who seek to disrupt operations or resort to extortion. Gamers too use DDoS as a means to gain competitive advantage and win online games.
There are clever cybercriminals who use DDoS as part of their diversionary tactics, intending to distract organizations during APT campaigns that are planned and executed in order to steal data.
How to prevent DDoS attacks
The first thing that needs to be done, to prevent DDoS attacks from happening, is to secure internet-facing devices and services. This helps reduce the number of devices that can be recruited by hackers to participate in DDoS attacks.
Since cybercriminals abuse protocols like NTP, DNS, SSDP, Chargen, SNMP and DVMRP to generate DDoS traffic, it’s advisable that services that use any of these ought to be carefully configured and run on hardened, dedicated servers.
Do repeated tests for security issues and vulnerabilities. One good example is doing penetration tests for detecting web application vulnerabilities.
Ensure that your enterprise implements anti-spoofing filters as covered in IETF Best Common Practices documents BCP 38 and BCP 84. This is because hackers who plan DDoS attacks would generate traffic with spoofed source IP addresses.
Though there are no fool-proof techniques that can prevent DDoS attacks completely, you can ensure maximum protection by ensuring proper configuration of all machines and services. This would ensure that attackers don’t harness publicly available services to carry out DDoS attacks.
It’s to be remembered that it’s difficult to predict or avoid DDoS attacks and also that even an attacker with limited resources can bring down networks or websites. Hence, for any organization, it becomes important that the focus is always on maximum level protection for enterprise networks, devices, websites etc.
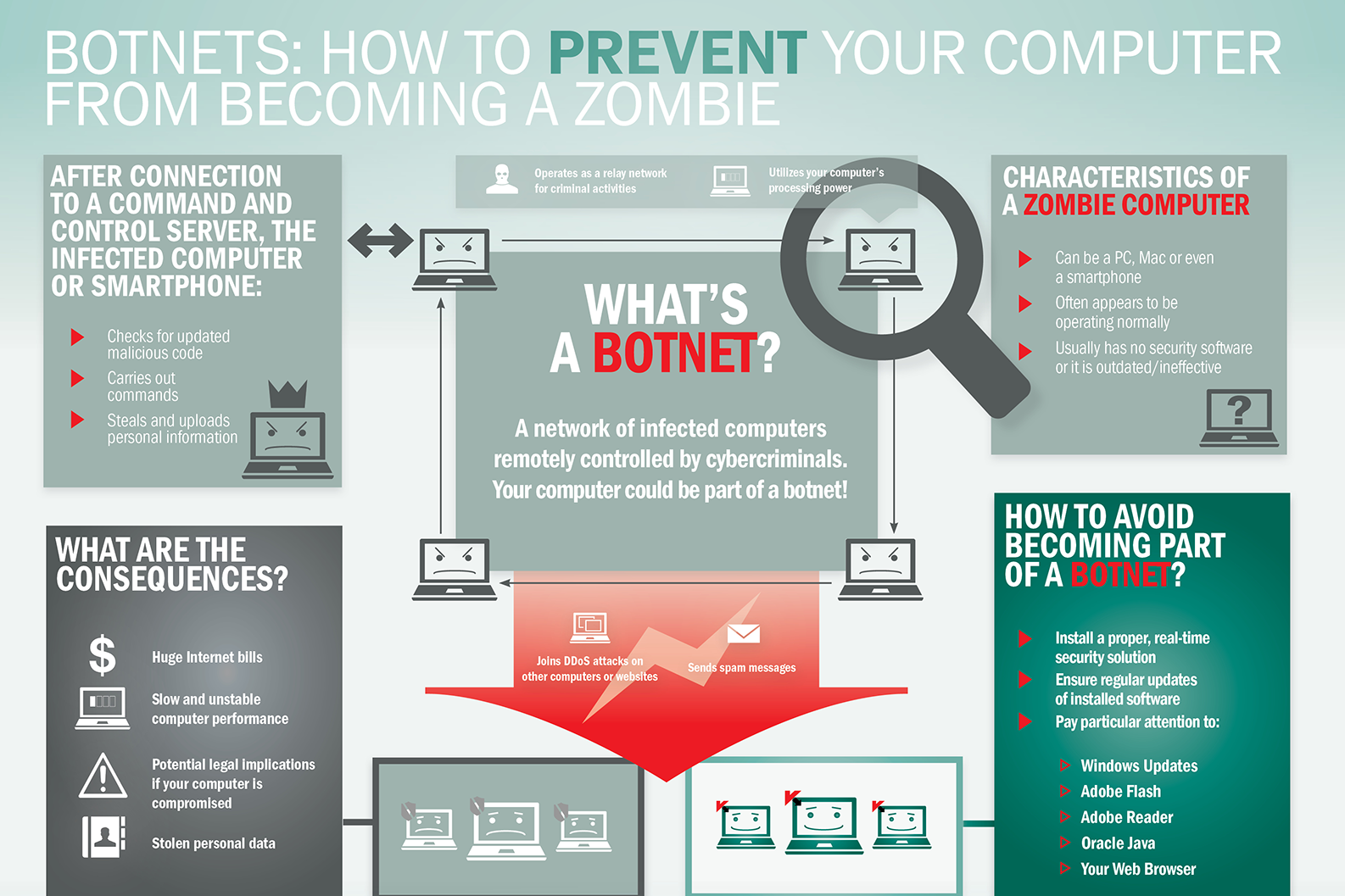
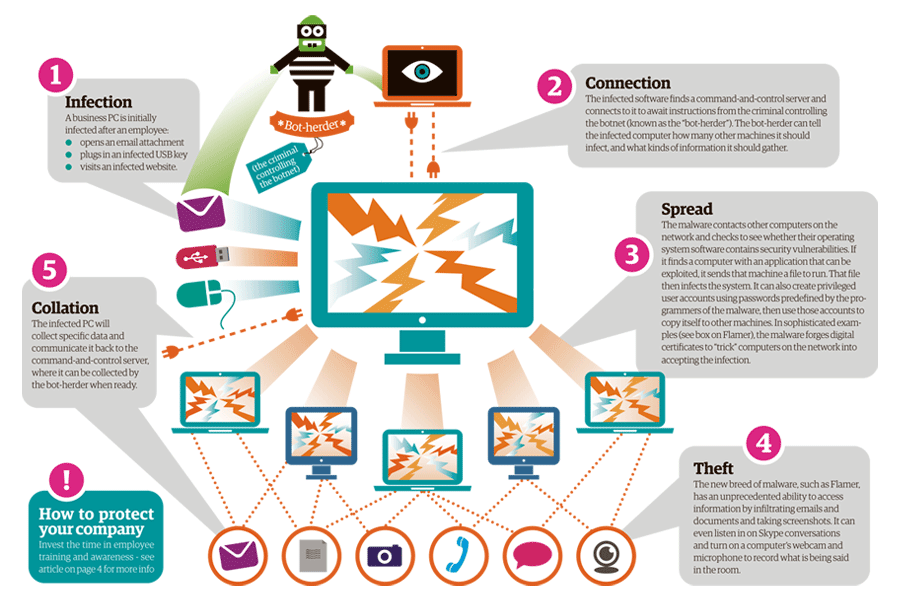
What is Botnet - Cybercriminals #1 Weapon
The word Botnet is formed from the words ‘robot’ and ‘network’. Cybercriminals use special Trojan viruses to breach the security of several users’ computers, take control of each computer and organise all of the infected machines into a network of ‘bots’ that the criminal can remotely manage.
Botnet Prevention- What is Botnet
How Botnets can impact you
Often, the cybercriminal will seek to infect and control thousands, tens of thousands or even millions of computers – so that the cybercriminal can act as the master of a large ‘zombie network’ – or ‘bot-network’ – that is capable of delivering a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, a large-scale spam campaign or other types of cyberattack.
In some cases, cybercriminals will establish a large network of zombie machines and then sell access to the zombie network to other criminals – either on a rental basis or as an outright sale. Spammers may rent or buy a network in order to operate a large-scale spam campaign.
How to prevent your computer becoming part of a Botnet
Installing effective anti-malware software will help to protect your computer against Trojans and other threats.
What advice does the world's first CISO have
What advice does the world's first CISO have for the current generation of CISOs? Stephen Katz emphasizes, first and foremost, that cybersecurity must be treated as a business risk management issue rather than a technology issue.
"Security has to evolve and grow at the same pace as the business," he stresses in an interview with Information Security Media Group.
The role of the CISO has to be recognized as a core business function, he adds. "Security has to be an enabler of the business; security has to earn a seat at the executive table. Too often, we give people the title of chief information security officer; they don't believe they're an executive, and executives don't believe they are an executive."
In this interview (see audio link below photo), Katz also discusses:
Changes in the threat landscape since becoming the world's first CISO;
Top priorities for CISOs in the coming year;
Why getting back to the basics of security remains so important;
The ongoing growth of machine learning models in all aspects of cybersecurity.
Katz is the founder and president of Security Risk Solutions LLC, an information security company providing consulting, mentoring, coaching and advisory services. He was formerly CISO at JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup and Merrill Lynch.
Secure Google Chrome from Hacking Attacks
Google Chrome is definitely one of the most popular web browsers being used today. Hackers, as we know, are perpetually after whatever gets popular in the world of the internet. This because whatever is popular would help them target more people and steal more data. Thus, Google Chrome too happens to be among the most favorite for cyber criminals across the world. Hence, securing Google Chrome against hacking attacks is really important.
So, how do we secure Google Chrome from cyber attacks? Well, it’s a multi-step process. Lots of things have to be done. Securing your browser is important as it helps secure your device, your internet connection and more importantly, your personal and business data.
Let’s discuss, in detail, what all needs to be done to secure Google Chrome from hacking attacks. Here we go:
Begin by ensuring that your Google account is properly secured!
This is something basic, your Google account needs to be properly secured. Chrome lets you sign in from any device, anytime. Hence, it’s important to ensure the security of your Google account. You need to make sure you are logged out of your account every time you sign in, on any device. You also need to ensure that your password is secure. If you aren’t signed out or if someone knows/cracks your password, it would be easy to manipulate things and cause you harm. Your data could be stolen.
Keeping the browser secured is equally important…
Keeping the browser secured is as important as securing your Google account. You could use a password to protect your browser, and thus, in your absence, no one would be able to take control of your browser and do mischiefs. Similarly, every time you leave your terminal, it’s good to go out of the browser as well.
Keep your browser ‘clean’!
You should make it a habit to keep your browser ‘clean’, by wiping out most of the information from it. In fact, there should be some plan/schedule as regards cleaning the browser. Clear the history periodically, either everytime you log out or at least once every week if not once a day.
Never save passwords on the browser
The browser might offer to ‘remember’ your passwords for you so that you could sign in easily the next time you’re using some service. But it’s always good not to save passwords on the browser. If you save your passwords, it would be possible for someone else to get into your account and misuse it or steal information.
Having a master password helps
Having a master password, which would help you get to your other saved passwords in Chrome, is a good thing to do. Thus you need not worry about remembering all of your passwords and you don’t have to be afraid of your passwords getting stolen or misused either.
Keep your device protected
The device that you use to browse needs to be protected from malware and hacking. For this, you must use whatever security tools you need and also have alerts that tell you if at all your device is compromised. Remember a compromised device means an unsecured browser!
Keep the device locked whenever you’re not using it
Always keep your device locked when you are not using it, be it a computer or any other mobile device. That prevents people from getting on to your device and hijacking your browser and your data as well. Locking your device also gets it off the WiFi network that you are using.
Secure your network, never use unsafe WiFi networks
Securing your network is important; it helps a lot in securing Google Chrome from hacking attacks. Hence you need to do all that is needed to secure your network. Similarly, it’s always advisable never to use unsafe WiFi networks. Whenever you’re using a WiFi network, ensure it’s properly encrypted and if possible use an app or program that would prevent hacking. In fact, using a secure network secures not just your browser, but everything on your device/system.
Trust Chrome for phishing detection
Google Chrome does its own phishing detection and protects you from many phishing websites. So, when your browser tells you that a website is not safe, it’s always advisable to trust it and avoid such sites.
Avoid phishing websites and attachments yourself
In addition to Google Chrome detecting phishing websites for you, it’s always good that you yourself stay away from websites/attachments that could be used for phishing scams. Staying away from such suspicious websites secures your browser, your system/network and your data.
Useful tips for implementing the cloud
Useful tips for implementing the cloud
“One very important thing is to not implement solutions on the cloud with a traditional mindset. Many clients are surprised when they see their first bill because they ‘lift and shift’ the infrastructure,”
“Remember, the cloud is highly elastic in nature and you can scale up and when you require. So, implement the minimum infrastructure needed and scale it based on load. That’s the secret to success in the cloud!”
Focus on entry and exit points in terms of network connectivity. Wherever possible, use private connections such as Microsoft express route, AWS direct connect.
In terms of cloud application connectivity, always encrypt the data in transit using SSL.
Ensure you implement least privileged and conditional based access to cloud administrative portals such as the Azure portal and AWS management console.
Implement RBAC access in providing access to cloud resources. Segregation and isolation of the resources using resource groups, virtual networks is key!
Utilise the security monitoring tools provided by cloud services provider to monitor the solution. Most of the basic functionality is free, such as Azure’s security centre.
In general, always divide the security focus areas into a matrix where rows are networks, compute, storage, applications, databases, and columns are data encryption at rest, encryption at transit, authentication and authorization etc; this will allow focussing on each security cell.
Carry out security risk assessment during the design phase to ensure the design has the appropriate security controls in place to mitigate possible risks.
Nevertheless, problems can arise when storing data in the cloud. “Services & data in the cloud is accessible from the internet. Unless proper controls in place, your users can access and download the data from anywhere in the world,” warns Varma.
Cloud storage security
“The majority of clients require their data to be encrypted in the cloud. Although cloud supports ‘bring your own key’ options, these encryption keys are stored in cloud providers key vaults. So, there is a very narrow chance that cloud providers can access those keys and decrypt the data. It’s also vital to note that cloud providers have very strict governance and accreditations in place to mitigate the same.”
Cloud providers generally keep their cloud services up-to-date with advancements in technology, according to Varma. “On the other end, many of the clients’ data centers he has worked within the past have out-of-date IT infrastructure systems & applications which takes a lot of time and money to replace and are prone to attacks”, he adds.
Varma also advises that you must ask your service provider the following questions about cloud storage security:
What is the authentication and authorization approach to cloud services?
How do you implement access controls for cloud services?
What’s the approach to secure transit and rest data?
What is preventive security monitoring are in place against risks and threats?
Are their solution adheres to such as cyber essentials, cloud security principles, ISO 27002?