CYBER SECURITY CONSULTING SERVICE AWARDS AND RECOGNITIONS
CyberSecOp's comprehensive managed security services, cyber security consulting, professional services, and data protection technology are recognized as industry-leading threat detection and response solutions by major analyst firms, key media outlets, and others.
VirusTotal Malware Analysis Tool VS Joe Sandbox VS Any.Run Malware Analysis Tool
What is a sandbox, and why do you need one to analyze malware?
A sandbox is an isolated computer and network environment designed for analyzing software behavior. This environment is typically designed to run risky files and determine whether those files pose a malware threat. Some sandboxes are also designed to examine URLs to determine whether they are suspicious and could lead to malware infection. Modern sandboxes enable businesses and individuals to test any type of file, including Microsoft Office files, PDF files, and executable files.
VirusTotal Malware Analysis Tool
Virus Total is an online service that uses antivirus engines and website scanners to analyze suspicious files and URLs in order to detect different types of malware and malicious content. It provides an API through which users can access the data generated by VirusTotal.
Cyber security and professionals use the free VirusTotal online service, but there is also a paid version that allows you to analyze files or URLs in order to identify malware detectable by antivirus engines, and it is one of the most popular in the community, so we decided to get a piece of that action.
Joe Sandbox Malware Analysis Tool
The free version of Joe Sandbox enables users to send files, browse a URL, download and execute a file or submit a command line. It works for Windows operating systems, macOS, Android, Linux, and iOS, making it a complete solution for customers with a large variety of operating systems in their IT infrastructure.
The only Windows systems accessible in the free version are a Windows 7 64-bit virtual machine and a Windows 10 64-bit physical machine. Other systems are available in the Cloud Pro service. Not many sandboxes offer the possibility of running files in a real physical system, which is one of the greatest features of Joe Sandbox.
ANY.RUN Malware Analysis Tool
ANY.RUN sandbox supports parsing public submissions. In this manner, an analyst can first search the database for any known indicator of compromise (IOC) and malware to see if it has already been publicly analyzed and then obtain the results. It contains millions of public submissions and is updated daily.
ANY.RUN's free version allows users to send files or URLs to a Windows 7 32-bit virtual machine, while the paid version allows users to send files to Windows Vista, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
The most powerful feature of ANY.RUN is the ability to interact in real-time with the virtual environment that runs the suspicious file or URL. Once a file is submitted, the user has 60 seconds to interact with the entire environment (or more on paid plans). This is a fantastic feature when analyzing malware that waits for specific user actions before running any payload. Consider malware that quietly waits for the user to launch a specific application (such as a browser) or to click on a dialog box. This is where the sandbox comes in handy.
What are some alternatives?
When comparing VirusTotal and Joe Sandbox, Any.Run you should also take into the following products.
Cuckoo Sandbox - Cuckoo Sandbox provides a detailed analysis of any suspected malware to help protect you from online threats.
Hybrid-Analysis.com - Hybrid-Analysis.com is a free malware analysis service powered by payload-security.com.
Jotti - Jottis malware scan is a free online service that enables you to scan suspicious files with several...
Metadefender - Metadefender, by OPSWAT, allows you to quickly multi-scan your files for malware using 43 antiviruses.
Falcon Sandbox - Submit malware for analysis with Falcon Sandbox and Hybrid Analysis technology. CrowdStrike develops and licenses analysis tools to fight malware.
What is Malware Analysis? Malware analysis is the process of determining the behavior and intent of a suspicious file or URL. The analysis' output aids in the detection and mitigation of a potential threat. Reverse engineering, sometimes called back engineering, is a process in which software, machines, aircraft, architectural structures, and other products are deconstructed to extract design information from them. Often, reverse engineering involves deconstructing individual components of larger products. Reverse engineering malware involves disassembling (and sometimes decompiling) a software program. Through this process, binary instructions are converted to code mnemonics (or higher-level constructs) so that engineers can look at what the program does and what systems it impacts.
SEC Proposes New Cybersecurity Rules
The SEC proposed to add new Item 106 to Regulation S-K and updates to Forms 10-Q and 10-K that will require public companies to provide periodic updates about previously disclosed cybersecurity incidents when a material change, addition or update has occurred.
These days cyber-attacks are common across all industries and sectors, however, the finance industry inclusive of fintech seems to be one of the most targeted by cyber-attackers and cyber criminals. In 2021, according to Statista, the finance industry was ranked as the second largest target for cyber-attacks being targeted four times more than healthcare and almost nine times more than government. Although most organizations in the finance industry have built formidable security programs, the inbound threats have also become much more frequent and sophisticated. As cyber-attacks constantly grow in number and sophistication, we see organizations being breached every day. According to J Makas at ThinkAdvisor.com, by 2023 an estimated 33 billion accounts will be affected by cyberattacks targeting the financial sector.
SEC in response to rising threats
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), in response to these rising threats and as a result of concerns voiced surrounding the lack of preparedness across the industry to advanced cyber-threats, has proposed new rules with a focus on standardizing and increasing cyber-reporting across the finance industry and public companies. The new rules proposed on March 9th of 2022 would require public companies to make prescribed cybersecurity disclosures. This proposal is an attempt to protect investors and strengthen their ability to evaluate public companies’ cybersecurity practices and incident reporting. cover IT risk management, cyber incident reporting, and cyber risk disclosure. The proposed rules would make cybersecurity a large part of the overall enterprise risk management
The proposed rules are an expansion on SEC’s previous guidance from 2011 and 2018 and would make material cybersecurity incident reporting, including updates about previously reported incidents as well as ongoing disclosures on companies' governance, risk management, and strategy with respect to cybersecurity risks, including board cybersecurity expertise and board oversight of cybersecurity risks, all mandatory.
In specific, the new rules would add cybersecurity incidents on Form8-K requiring organizations to disclose all cybersecurity incidents and identified risks. The information required on the Form 8-K would cover (a) the timing of cyber-incidents and whether they are resolved or ongoing, (b) required brief details on the nature of the incident, (c) a report on any affected data even if the data was not exfiltrated, d) effects of every cyber incident on the organization’s operations, and e) information on remediation activity. One interesting item of note is that the actual date the cyber-incident began will be required and not just the date it was discovered.
Require companies to disclose
Also, the new rule would require companies to disclose the following in form 10-K:
· Does the company have a cybersecurity risk assessment program and if so, provide a description of such program;
· Does the company engage assessors, consultants, auditors or other third parties in connection with any cybersecurity risk assessment program;
· Does the company have policies and procedures to oversee and identify the cybersecurity risks associated with its use of any third-party service provider (including, but not limited to, those providers that have access to the company's customer and employee data), including whether and how cybersecurity considerations affect the selection and oversight of these providers and contractual and other mechanisms the company uses to mitigate cybersecurity risks related to these providers;
· Does the company undertake activities to prevent, detect, and minimize the effects of cybersecurity incidents;
· Does the company have business continuity, contingency and recovery plans in the event of a cybersecurity incident;
· Have previous cybersecurity incidents have informed changes in its governance, policies, procedures, and technologies;
· How and whether cybersecurity-related risks and incidents have affected or are reasonably likely to affect its results of operations or financial condition and if so, how; and
· Cybersecurity risks are considered a vital part of its business strategy, financial planning, and capital allocation and if so, how.
requires cyber risk management to be identified in the organization's 10-K form
The proposed rules will also require information on the company’s cybersecurity governance, board oversight of the cybersecurity risks, and how cybersecurity risks are managed and assessed to be present in the company’s form 10-K as well as in annual reports. Companies will also be required to identify any members of the board with expertise in cybersecurity including their names and a full description of the nature of their expertise. Besides these requirements, there will also be disclosure requirements to tag any data that at any point was considered to be affected in any way by a cyber-incident. Lastly, foreign private issuers ("FPI") will also have mandatory incident disclosures to make.
These rules proposed by the SEC are meant to provide more visibility to investors as well as the federal government, thereby protecting investors as well as standardizing the level of cybersecurity and IT risk management programs across public companies and the finance industry. It is likely that Congress as well as entities such as the SEC will not stop here and will continue to propose further cybersecurity and IT risk management related regulation.
What are Cyber Security Services?
What is cyber security?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices and technologies used to protect computers, networks, and devices from cyber-attacks and threats. Cybersecurity is critical because it helps to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and systems. Cyber attacks can come in many forms, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. They can have serious consequences, including the theft of sensitive data, the disruption of business operations, and the loss of money. To protect against these threats, organizations, and individuals can use a variety of cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and strong passwords. It is also essential to educate users about how to recognize and avoid cyber threats and to keep software and systems up to date with the latest security patches.
What are Cyber Security Services?
There are many different types of cybersecurity services that organizations and individuals can use to protect themselves against cyber threats. Some examples of cybersecurity services include:
Managed security services: These services provide ongoing monitoring and protection of an organization's networks and systems by a team of cybersecurity experts.
Network security: This type of service protects an organization's networks from external threats, such as hackers and malware.
Cloud security: This service helps to secure an organization's data and applications that are hosted in the cloud.
Email security: This service helps to protect against threats that are transmitted through email, such as phishing attacks and spam.
Endpoint security: This service helps to protect the devices that are used to access an organization's networks and systems, such as laptops and smartphones.
Web security: This service helps to protect an organization's website and web-based applications from threats such as malware and hacking.
Identity and access management (IAM): This service helps to ensure that only authorized users have access to an organization's systems and data.
Compliance and risk management: This service helps organizations to comply with relevant laws and regulations and to manage their cybersecurity risks.
Incident response: This service helps organizations to respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents, such as data breaches and cyber attacks.
What is security compliance?
Security compliance refers to the process of following rules, guidelines, and standards that are designed to protect an organization's information and systems from cyber threats. These rules and standards may be mandated by laws and regulations, or they may be voluntary industry standards. Some examples of security compliance frameworks and standards include:
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This standard applies to organizations that accept, process, or store credit card payments and is designed to protect against the theft of cardholder data.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): This law applies to organizations in the healthcare industry and sets standards for protecting patient health information.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This law applies to organizations that process the personal data of individuals in the European Union (EU) and sets standards for data protection and privacy.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework: This framework guides organizations on how to manage and reduce their cybersecurity risks.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001: This standard provides a framework for an organization's information security management system (ISMS).
Following security compliance standards can help organizations to protect their information and systems from cyber threats and avoid fines and other penalties for non-compliance. It is important for organizations to assess their compliance with relevant standards regularly and to implement measures to address any gaps.
Managed security service providers (MSSPs)
Managed security service providers (MSSPs) are companies that offer a range of cybersecurity services to organizations on a subscription basis. These services may include ongoing monitoring and protection of an organization's networks and systems, incident response, and compliance assistance. MSSPs can help organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of cyber attacks in several ways:
Expertise: MSSPs typically have teams of cybersecurity experts with the knowledge and experience to identify and mitigate potential threats.
Continuous monitoring: MSSPs can provide continuous monitoring of an organization's networks and systems, which can help to identify and respond to threats in real time.
Time and cost savings: Outsourcing cybersecurity to an MSSP can save an organization time and resources that would otherwise be spent on in-house cybersecurity efforts.
Compliance assistance: MSSPs can help organizations to ensure compliance with relevant security standards and regulations.
By working with an MSSP, organizations can benefit from the expertise and resources of a dedicated cybersecurity team, which can help to improve their overall security posture and reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
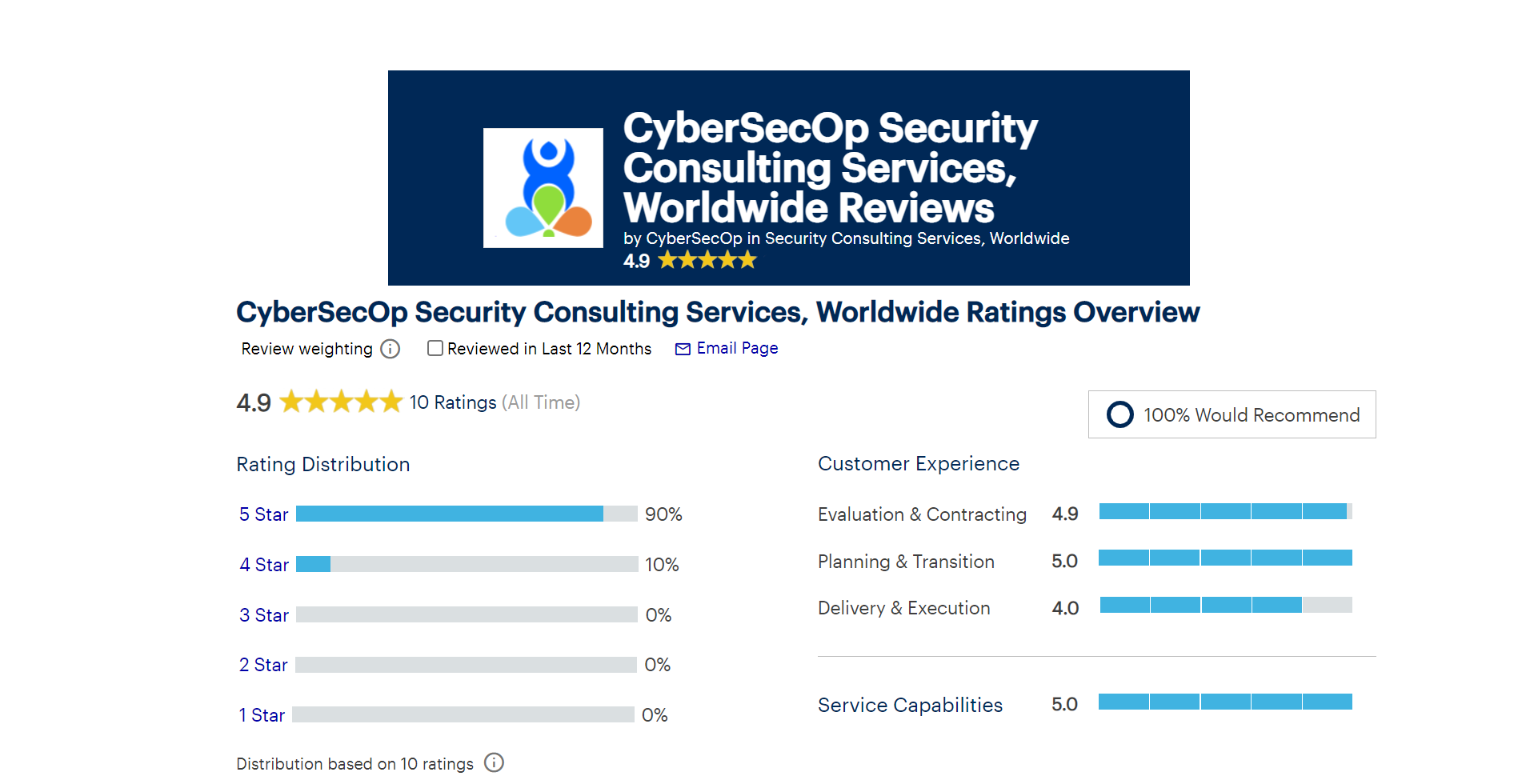
Gartner Recognizes CyberSecOp - Ranked 2nd for Security Consulting Worldwide.
CyberSecOp receives the highest overall score on Gartner Peer Insights for Security Consulting Services, Worldwide in 2022.
June 8, 2022 - CyberSecOp today announced that its Security Consulting Services received a 4.9 out of 5 overall rating from Gartner Peer Insights, placing CyberSecOp in the top two on Gartner’s Security Consulting Services Worldwide category.
"Peer reviews are extremely valuable for evaluating any purchase decision," said Josh Bauer, Executive Director at Loxo Oncology/Lilly. “CyberSecOp appears to actively and continuously listen to us as a customer to ensure they deliver innovative solutions and a valuable user experience."
“CyberSecOp is honored to receive our current ranking status and client feedback, and we will continue to prioritize customer satisfaction across the board." Vincent LaRocca, CEO & Co-Founder.
2022 Gartner Peer Insight
Gartner Peer Insights is the firm's platform for rating and reviewing enterprise technology solutions by end-user professionals for end-user professionals. Through user-contributed reviews from people who have actually used the services, the rating system combines expert opinions and peer insights. Peer Insights User Reviews offers a suite of interactive features for technology buyers, including the ability to customize evaluation criteria to create a quadrant view tailored to the user's goals and priorities. The platform employs rigorous methodologies, processes, and quality standards to deliver unbiased research and authentic peer reviews.
What is Gartner’s research?
Gartner research: Trusted insight for executives and their teams
Gartner research, which includes in-depth proprietary studies, peer and industry best practices, trend analysis, and quantitative modeling, enables us to offer innovative approaches that can help you drive stronger, more sustainable business performance.
Gartner research is unique, thanks to:
Independence and objectivity
Our independence as a research firm enables our experts to provide unbiased advice you can trust.
Actionable insights
Gartner’s research is unbiased, containing vital takeaways and recommendations for impactful next steps.
Proprietary methodologies
Our research practices and procedures distill large volumes of data into clear, precise recommendations.
What is Cybersecurity & Security Risk Assessment?
CYBERSECURITY & SECURITY RISK ASSESSMENT
Cybersecurity encompasses the functions, actions, processes, tools, and resources utilized in securing one’s digital presence and cyber network of connected systems, data, and devices. It aims to reduce risk to an organization or entity continuously. It is a complex endeavor where the effort is constant, the dangers are abundant, and visibility is key. Visibility is knowledge, its power, and it can be the difference between staying in business or going out of business. It is the difference between making your customers and clients live better or unintentionally much worse, providing for your employees with a good living or adding to unemployment, and focusing on growing your organization or worrying about how to pay regulatory fines. Yes, visibility is all that and more.
Cybersecurity & Security Risk Assessment Benefits
Now that we’ve established that visibility is essential, let’s look at what it means in the cyber-realm. Visibility is to cyber what doors, windows, locks, roofs, basements, weapons, and fighting or defensive resources are to a zombie attack. Imagine this: you’re in a big house with many rooms, doors, windows, etc., and you are under a zombie attack. You run and close the garage door, lock the front and back doors, shut the windows, and believe you are safe. But you had no idea the roof is only an inch thick and caves in with the slightest weight or some room somewhere in the house had an extra window, and it’s wide open. Think about how all the effort you put into closing all those other doors and windows just went to waste because you missed one and how important it would have been to have known all of that. Game over, right?! That is the power of visibility. Gain knowledge of every weakness and strength and all factors that can potentially become routes to attack or provide defenses.
Cyber Attacks Prevention
In the efforts of ensuring data and systems are protected from cyber-attacks and the plethora of federal, state, and international regulations are met, one of the most powerful tools that provide the needed visibility is a Security Risk Assessment. A Security Risk Assessment conducted by an experienced third party is absolutely key to providing vital visibility into the entire organization’s strengths and weaknesses. But that’s not where a Security Risk Assessment ends. When correctly done, Security Risk Assessments go much further and provide detailed roadmaps to close the identified gaps and maximize the recognized strengths. Security Risk Assessments also hold an organization’s hand and walk them through which gaps pose the most significant risk; and which ones will cost the most or the least. This provides precise risk analysis, ranking all the gaps and risks in detail.
When a third-party Security Risk Assessment is completed and presented, it should provide comprehensive guidance. The guidance offers complete visibility into all you didn’t know, confirmation of what you may have known, and precise advice on achieving a better and more mature security posture inclusive of all the proactive and reactive measures needed.
It's no wonder every Security Framework, international, federal, and state regulation involving IT risk management and cybersecurity emphasizes Security Risk Assessments as a must-have. Don’t be blind to potentially devastating gaps in your organization. Contact us and get your Security Risk Assessment. Cyber-attackers are not waiting, and neither should you.
Author: Carlos Neto
Healthcare is a Top 3 Cyber Target
Attacks on the healthcare industry are on the rise as noted in a recent article published in CYBERSECOP. Healthcare providers of all sizes are subject to attack and in this case, CHRISTUS Health learned of “unauthorized access” likely similar to 254 ransomware incidents targeting patient care facilities between June 2020 and April 2022 worldwide. Patients are at risk, both their health and their PII where threat actors can alter and/or add to patient billings with no notice of impropriety. The true impact will be hard to discern until more time and data are collected but we know one thing for sure, the healthcare industry needs to take cybersecurity as seriously as they do patient care and follow their own advice; Plan, Prevent, Protect and Respond.
Plan – Get a Risk Assessment to identify and understand your cybersecurity vulnerabilities is one of the most critical steps as the awareness will lead to a prioritized remediation plan. Even a chink in the armor will have your patients, employees, and community concerned as a cyber-attack will likely affect critical operations because the prize is financial data, patient, and employee Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
Prevent - After an assessment is completed, you need a trusted and reliable security cyber organization to assist in leveraging the right framework and controls to be measured by such as HITURST, HITECH, HIPAA and PCI. These guidelines assist in defining the appropriate critical security controls for effective cyber defense. These efforts can be awareness training, policy creation & enforcement, and security controls as well as incident response readiness and governance. It’s a journey, not a sprint.
Protect – Within most remediation plans include investments in endpoint protection dark web monitoring and focusing on digital trust goals to ensure the technology investments already made as well as those in the future work in harmony. Like a Rubik’s cube, the goal is to have every facet of your organization in order, not just celebrating a single win. It is important to have a managed security partner to protect your patients, employees, devices, and data with monitored protection systems along with managed & encrypted backups with a Security Operations Center staffed with certified security professionals watching and engaging on your behalf 24x7x365.
Respond – Did you know that a threat actor will live in your ecosystem for an average of 121 days mining sensitive data, passwords, organization charts, and behaviors before acting? Nearly 95% of ransomware attacks are preventable so what starts as a threat becomes a technology issue, then a business risk issue, and eventually decision-making and communications issue at the board level. Do you pay the ransomware or not? Are we able to recover our data? Has the threat actor accessed our PII? And equally important is how do you keep from reaching this point again. Having an incident response assessment and plan might be the one thing you do if you don’t buy into everything else. You should receive an IT assessment of “how capable are we to thwart an attack?” and “how able are we to recover if breached?” Buying cyber insurance is not the silver bullet it used to be so having an incident partner who is proactively focused on your company’s sensitive data and reputation is paramount.
Not unlike a hospital, there are two main ways to address cyber security by coming through the Emergency Room or the front door proactively for testing; I recommend the latter. A proactive health check is the best step to understanding your ability to fight off an attack like a stress test. The results may drive adjustments in behavior and readiness, such as point endpoint detection, policy creation & enforcement, and security training. If you enter the ER, then don’t panic because you read this blog and signed up a reputable security partner to react & respond, including quarantining affected systems to prevent the ransom spread, resetting all passwords, checking your backups, activating your existing crisis/DR plans and negotiate with the threat actor if that is the best business decision communicating carefully along the way with detailed documentation. The moral of this story is that hope is not a strategy, so know your security scorecard and realize cyber readiness is a journey, not a sprint.
Author: Christopher Yula
Don't let a cyber security breach damage your reputation
Cybersecurity breaches have cost many organizations some of their largest clients. While most organizations quickly hire legal experts, public relations teams, and a cyber security firm like CyberSecOp, the reputation damages have already begun. For example, your client may not have access to your services for hours before you realize that your system was affected.
Prime attack time
Attackers are strategic with time selection to minimize their activities being seen by employees. Most attackers operate on weekends or at night, knowing that most organizations’ employees do not access or monitor systems at this time.
When does reputation damage begin?
Reputation issues may begin long before the organization knows about an attacker. Some attackers disclose information on social media so that the organization will act quickly to their demands. Most cybercriminals spend an average of three months on clients’ systems before they act, but by this point, they may have already sold your data on the dark web or to your competitor.
Disclosing sensitive information violates privacy policies and requirements such as CCPA, GDPR, and some states’ and countries’ data protection regulations or requirements. The data disclosed may also include clients and your client’s customer information, putting your clients at risk. They, too, need to report the breach to their customers and provide the necessary protection to protect their customer’s credit and identity.
Reputation damage extends to your client.
At this point, not only is your organization’s reputation is in jeopardy, but also the reputation of your client and your client’s customers. All of these expenditures may be a liability to your organization if the breach is on your side, especially if there is evidence that you didn’t take due care regarding your organization’s security posture.
Conclusion
Defense-in-depth security program
Having a defense-in-depth security program such as those offered by CyberSecOp, cannot only save your business money but can also help you compete against other companies that have not implemented a security program. Most organizations have implemented a vendor management program to mitigate their threat against a third-party risk. A security program that includes third-party risk management is critical to identifying and remediating internal and external threats.
Sanctions Leave US Ransomware Victims with No Way Out
The US Treasury Department's Office of Foreign Assets Control ("OFAC") imposed multiple sanctions against a Russian-operated virtual currency exchange involved in ransomware payments. It issued an updated advisory on the sanction risks associated with ransomware payments.
Victimized organizations balance the risk and cost of stalled operations and encrypted data with federal watchdogs ready to act. Response and recovery are never going to be an easy process. Ransomware exists because organizations and cyber insurance companies are paying the perpetrators.
Ransomware attacks, in most cases, cause complete shutdowns of mission-critical functions. This has the same effect as business continuity events. As a result, business continuity planning is one of the best ways to prepare for the increasing likelihood that an organization will eventually fall victim to a ransomware attack. Without a solid business continuity plan, organizations are forced to pay threat actors and may face stiff sanctions or fines in the future.
A ransom payment is a negligible portion of the costs incurred by an organization following a ransomware attack. Added to the risk of reputation loss, fines, sanctions, downtime, and recovery expenses, organizations, and cyber insurance firms face uncertainty without clear direction on identifying threat actors for proper OFAC due diligence.
Biden-Harris Administration Warns
In response to the unprecedented economic sanctions imposed by the United States, the Biden-Harris Administration has repeatedly warned about the possibility of Russia engaging in malicious cyber activity against the United States. There is now growing evidence that Russia is considering cyberattack options.
The United States Government will continue to work to provide resources and tools to the private sector, including through CISA's Shields-Up campaign. While we will do everything possible to defend the Nation and respond to cyber-attacks, the private sector owns and operates much of the nation's critical infrastructure. Therefore, the private sector must act to protect the vital services on which all Americans rely.
Biden-Harris Administration and CISA Urge Companies To
Below you will find a list of guidance provided by the Biden-Harris Administration and CISA. CyberSecOp has assisted with the following list, along with other security frameworks found below.
Biden-Harris Administration and CISA List
Mandate the use of multi-factor authentication on your systems to make it harder for attackers to get onto your system.
Deploy modern security tools on your computers and devices to continuously look for and mitigate threats.
Check with your cybersecurity professionals to make sure that your systems are patched and protected against all known vulnerabilities and change passwords across your networks so that previously stolen credentials are useless to malicious actors.
Back up your data and ensure you have offline backups beyond the reach of malicious actors.
Run exercises and drill your emergency plans so that you are prepared to respond quickly to minimize the impact of any attack.
Encrypt your data so it cannot be used if it is stolen.
Educate your employees about common tactics that attackers will use over email or through websites and encourage them to report if their computers or phones have shown unusual behavior, such as uncommon crashes or operating very slowly.
Engage proactively with your local FBI field office or CISA Regional Office to establish relationships before cyber incidents. Please encourage your IT and Security leadership to visit the websites of CISA and the FBI, to find technical information and other valuable resources.
Bolstering America’s cybersecurity over the long term
We also must focus on bolstering America’s cybersecurity over the long term. We encourage technology and software companies to:
Build security into your products from the ground up - “bake it in, don’t bolt it on” - protect your intellectual property and your customers’ privacy.
Develop software only on a highly secure system and accessible only to those working on a particular project. This will make it much harder for an intruder to jump from system to system, compromise a product, or steal your intellectual property.
Use modern tools to check for known and potential vulnerabilities. Developers can fix most software vulnerabilities — if they know about them. There are automated tools that can review code and find most coding errors before software ships, and a malicious actor takes advantage of them.
Software developers are responsible for all code used in their products, including open-source code. Most software is built using many different components and libraries, which are open source. Make sure developers know the provenance (i.e., origin) of components they are using and have a “software bill of materials” in case one of those components is later found to have a vulnerability so you can rapidly correct it.
Implement the security practices mandated in the President’s Executive Order, Improving our Nation’s Cybersecurity. Under that EO, all software the U.S. government purchases are now required to meet security standards in how it is built and deployed.
CyberSecOp Cybersecurity Services & Information Security Compliance assists organizations in developing mature cyber security, risk, and compliance programs according to PCI, HIPAA, SOC, GLBA, FISMA, ISO, NYDFS, NIST, and other security compliance mandates.
Protecting Against Ransomware: Zero Trust Security
Zero trust isn't a silver bullet for ransomware, but if implemented well, it can help create a much more robust security defense.
Did you know only 26% of companies have a specific incident response plan for ransomware? With ransomware attacks constantly on the rise, your organization needs to be prepared and take every possible precaution.
Reduce your organization’s risk with CyberSecOp Zero Trust Program. With the help of a single-source platform for your compliance program, you can protect against vulnerabilities while reducing incident response time by as much as 60%.
Ransomware victims paid more than $600 million to cybercriminals in 2021. According to blockchain analysis firm, Chainalysis, more than $600 million in cryptocurrency could be tied to ransomware payments in 2021, with the Conti ransomware gang accounting for nearly one-third of those payments.
HOW CAN CYBERSECOP HELP YOUR ORGANIZATION BE CYBER READY?
CyberSecOp provides cyber risk and advisory programs that identify security gaps and build strategies using Zero Trust or other security frameworks. The zero-trust model is an effective defense mechanism for preventing ransomware. Adoption of zero-trust architecture, the modern alternative to perimeter-based security, is one of the most effective ways to prevent ransomware attacks.
Don't Forget the Fundamentals on World Backup Day 2022
March 31st is apparently world backup day! Who knew? In honor of that it seemed like a good time for a quick post extolling the virtues of backups. According to the “WorldBackupDay” website, 21% of people have never taken a backup and 30% of computers are already infected with malware. While these stats are related to individuals and not necessarily businesses the stats sound about right.
Take Backups!
Regardless of whether you are a small business or a global Fortune 500 company, backups are an essential part of your organization's risk management plan. It’s easy to be lulled into complacency. Just the other day I was working with an organization in the mechanical service delivery industry who’s entire “IT Infrastructure” was a single 2017 iMac. They never bothered with any additional machines, backups and other such items because they had been told that Mac’s were “bulletproof” and not susceptible to the common maladies of the humble PC. Unfortunately, their Mac was susceptible to good old fashioned old age and corrupt updates. As a result they found themselves in a position where they had a large proposal for a job due the next day and the only place it existed was on this one broken Mac. Now fortunately for them, we were able to recover the system and restore their data, but what if we hadn’t been able to? It is absolutely critical, regardless of the size of your organization that you have a backup solution in place tailored to your specific needs. Stay tuned for some suggestions on backup providers we love at the end of this article!
Test your Backups!
This might seem like a no-brainer, but in addition to taking backups, it's critically important that you TEST your backups. Having a plan and procedure in place for how to recover your data in the event of a disaster is just as important as taking the backup in the first place! In my last example of the company with a single iMac. What if they had set up icloud and automatically configured their file to sync there. If I had asked the owner of the business if he had the password for the icloud account or even knew what account icloud was associated with, I wonder if he would have known? Having a documented plan that outlines where your backups go, what authentication is used to access them, how frequently they are taken, and how to restore them to a device is critical. If you are a larger organization you probably want to start having conversations about RTO and RPO at this point as well and ensuring your backup solution can meet those goals. (Recovery Time Objective, Recovery Point Objective.) Essentially, how long will it take to recover my data and how much time passes between backups, or put more simply, how much data can I afford to lose? 1 Day’s Worth? 1 Weeks worth? Less? More? Make sure your backup solution can meet your specific needs and goals!
Protect your Backups!
Finally, congrats if you're taking and testing your backups! Are you also protecting your backups? You’re probably thinking, protecting my backups?! What’s this guy going on about now? Consider this, you backup your information every night and test it regularly. You sleep easy at night knowing that you can recover should the worst happen. However, what you don’t know, is that earlier last month one of your employee’s laptops was infected with a virus. This virus replicated across your organization but stayed dormant, collecting information about your company and environment but not taking any malicious actions yet. The threat actor discovers that your backups run nightly and are stored for 4 months on a network share. The virus then deletes all of your backups and begins encrypting your files. When you return to work the next day and find all of your computers and files encrypted, you attempt to recover from backup only to find your backups have been deleted! This is an oversimplification of the process but this is essentially what the bad guys are doing. There are many ways to prevent this sort of attack including storing backups in offline or immutable data stores, encrypting your backups and storing multiple copies of every backup in different locations. At this point you might be thinking “I can simply copy files to an external drive of some sort on a regular basis right?” , but what if something happens to that drive? As the old timer’s say, “two is one and one is none”. The idea is that if you only have one, something could happen to it and then you have none. Have a backup plan for your backup plan!
Conclusion
Now that you’re completely terrified know that there are solutions out there for all of these problems. Proper backup planning is a key component of every organization's Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity and Incident Response Planning. If you are looking for assistance with any of those plans, make sure you give us at CyberSecOp a call, we would love to help you with this.
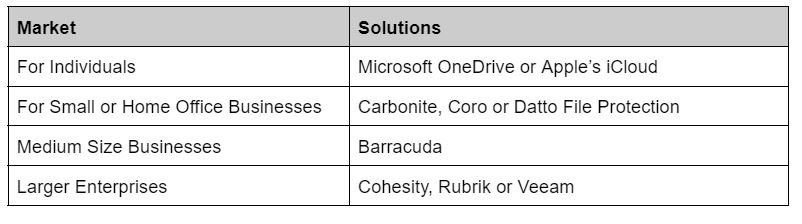
In the meantime if you're looking for somewhere to start with backup’s here are some of our favorites.
Author: Timothy Burger
Chrome and Edge Should Be Updated Due to a Zero-Day Vulnerability
Google and Edge has released an update to remediate a critical zero-day chrome exploit. The zero-day is a weakness in Edge and Chrome's JavaScript engine that can be used by hackers to inject their code into your browser. Google explains for zero-day exploit CVE-2022-1096, first reported to the company by an anonymous tip on March 23. As part of our commitment to continuous support in security monitoring and enhancement we advise all clients to update to Chrome version 99.0.4844.84 and Microsoft Edge 99.0.1150.55 of as soon as possible.
DETAILS AND REMEDY FOR MICROSOFT AND GOOGLE
At this time Microsoft and Google won't provide much more information other than admitting there have already been attacks leveraging this zero-day weakness and keeping some information away from the public as a safety measure, stating that full details on how the exploit worked won't be made public until most users have the fix. Fortunately, this time Microsoft and Google was apparently able to issue a patch before the exploit became widely known.
Normally Chrome updates happen in the background when you close and reopen your computer's browser.
Microsoft issued its own notice and said the issue was fixed in Edge.
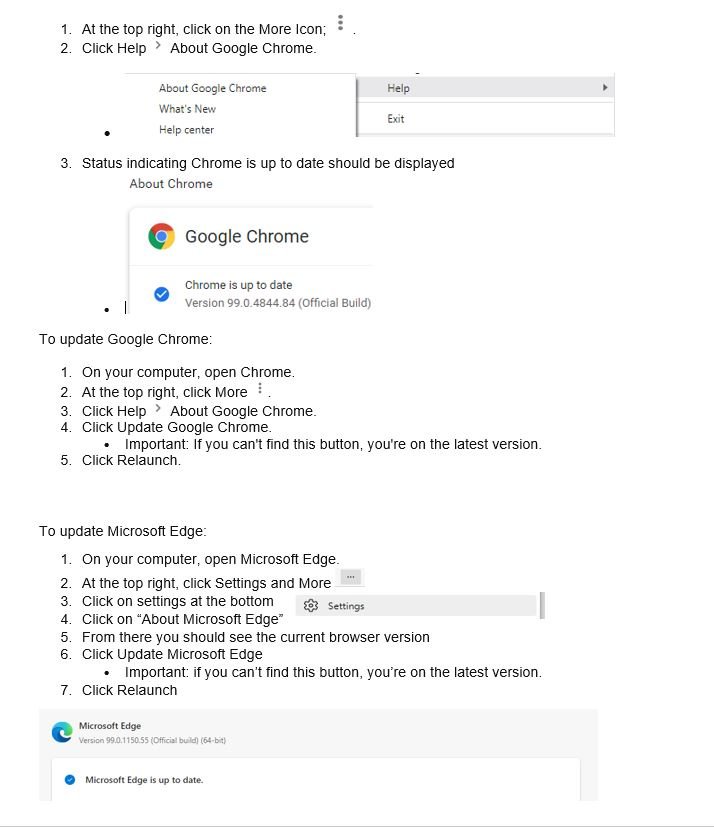
Please follow the steps below to ensure you have the latest version of Chrome.
Remediation Efforts
On your computer, open Chrome.
Author: Tanvir Ahmed
ADVISORY: Reports of possible digital breach
ADVISORY: Reports of possible digital breach
Okta investigating reports of possible digital breach
Lapsus$, a cyber extortion gang, has announced that they have breached Microsoft and Okta.
The gang has leaked torrents containing source code for Bing, Bing Maps, and Microsoft Cortana, as well as a screenshot of an internal Microsoft Azure DevOps account. They also claim to have had “Superuser/Admin” access to Okta’s systems for two months, and said its focus was “only on Okta customers.”
Both Microsoft and OKTA have started an investigation to confirm or disprove they’ve been breached.
Recommended Actions:
These attacks are a striking reminder of the supply chain’s cyber risks - Real risks brought to organizations by use of softwares and systems like OKTA, Microsoft, as well as many others.
Please work with your vCISO or Risk Manager to ensure the proper Vendor Security controls and processes are in place as well as other vital security controls that will drastically reduce the possibility of these dangerous hacks spilling into your network and systems.
Author: Michael Sardari
CISA's 'Shields Up' Alert Highlights Foreign Cyberthreats
Cyberwarfare is the battlefield of today. Increased geopolitical tensions stemming from Russia's unprovoked attack on Ukraine has led to CISA (the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency) issuing a "Shields Up" bulletin. Every organization must be prepared to respond to disruptive cyber activity, especially those in critical infrastructure fields.
Here are some tips to help you keep your organization safe in these trying times.
Reduce the likelihood of a damaging cyber intrusion
Use MFA or Multi-Factor-Authentication everywhere.
Ensure all Systems are patched and up to date.
Consider increasing patch frequency if not already real-time.
Take steps to quickly detect a potential intrusion
Run, update and monitor a strong Endpoint Protection Program.
Consider increasing Spam and Phishing filter sensitivity.
Disable any non-essential ports and protocols, specifically through external gateways.
Ensure that the organization is prepared to respond if an intrusion occurs
Review your incident response plan and ensure it is up to date and all parties are clear on their roles.
Maximize your organization's resilience to a destructive cyber incident
Ensure that you are taking regular backups and that your backups are encrypted and immutable.
Test your backup and recovery procedures.
Communicate with your users, the best and strongest defense is a well-educated and well-prepared workforce.
If you are a CyberSecOp customer today in either our vCISO or vSOC program your risk manager will be reaching out shortly to ensure this guidance is being implemented to the extent possible within your organization.
If you are not currently enrolled in one of our plans and need assistance assessing your posture and capabilities, please feel free to reach out.
What Does Cybersecurity Compliance Mean?
Cybersecurity Compliance involves meeting various controls (usually enacted by a regulatory authority, law, or industry group) to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. This is usually driven by a security consultant.
What is a Security Consultant?
A security consultant, also sometimes called a security analyst, pinpoints vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and software programs and identifies solutions to defend against hackers. This consultant role is a strong example of a highly specialized IT occupation.
What Does a Cybersecurity Consultant do?
Cybersecurity consultants assess an organization's security operations, computer systems, network, and software for vulnerabilities, then design and implement the best security solutions for the company. If a cyberattack does happen, the client will reach out to a security consulting firm, such as CyberSecOp, to seek expertise to respond and mitigate the damage. Cybersecurity consultants and risk managers can provide your organization with technology controls, policies, procedures and other management controls.
What does a Risk Manager do?
While cyber security consultants/analysts are geared more towards the technology stack of an organization a Risk Manager takes it a level higher and focuses on the organization risk from a holistic view. A risk manager can help an organization understand how to formulate a documented Risk Management Framework (RMF) in which representation from key stakeholders and leaders take part in continuously assessing, identifying and mitigating risks for the organization. This goes beyond the security tools and into the realm of Policy, Culture, Procedure, Communication and continuous improvement. Risk Managers are skilled at organizational risk and are a key component of not only ensuring compliance, but risk reduction as a whole. It is important to remember that being compliant is not necessarily being secure, and risk mangers can bring that whole package together.
What are Cybersecurity Consulting Services?
Cybersecurity consulting helps organizations mitigate certain risks and prevent identity theft, hacking and data theft. A cybersecurity consultant can also help identify risks that the business may have previously overlooked. Cybersecurity consulting acts as an extension to your in-house security team.
Main Areas of Focus Will Be:
Security management, governance and compliance
Risk Management
Security monitoring
Security architecture
Incident response
Remediation of attacks
Attack detection
Cybersecurity Consulting Service Benefits
Cybersecurity consulting acts as an extension to your in-house security team.
The professionals from CyberSecOp security consulting services can identify problems within the organization
Maximize your security investments with cybersecurity services.
Cybersecurity consulting management makes it easier to handle regulatory and compliance requirements.
Cybersecurity services provide you with experts who have the training, experience and qualifications needed to identify and manage risk all the while ensuring your business remains compliant.
CyberSecOp security consulting services help your organization achieve maturity within your security environment. CyberSecOp cybersecurity consulting firm has experience with diverse clients across many industries. A skilled group of security consultants will know the pitfalls and hurdles to avoid in relation to your security transformation or security compliance requirements.
CEO Letter - Cyber Security Operations Consulting (CyberSecOp)
Vinny La Rocca
Chief Executive Officer
We believe the foundation of our success is grounded in our vision to uplift enterprise security while ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability beyond best practices. That purpose is a virtuous circle. We create long-term value by empowering our people to deliver for our customers and communities. CyberSecOp helps organizations with security consulting, incident response and ransomware negotiation, payment, and recovery.
Our vital role to the community can be found in our mission statement. Our mission is to make the world a better place by defending and protecting our clients and partners from the theft of sensitive data through rapid incident response, cyber security programs, threat hunting, and the deployment of protective measures.
Sustainability and Growth
Our sustainability is rooted in our vision and mission statement. We believe this is an integral part of our growth and the reason we can keep our promises to our clients and partners.
Growth - Expectations for 2022 are higher than 2021, a year with 85% growth. Cyber risks currently rank as one of the top global threats to businesses and custodians of data, along with an ever-increasing number of data privacy and protection laws. These factors, combined with CyberSecOp’s ability to respond both proactively and reactively, put the company in a very favorable position.
Partnerships - CyberSecOp continues to develop, encourage and align an increasing number of strategic partnerships, allowing our teams to continually improve upon our Service Level Agreements (SLA’s) and expand our portfolio and breadth of services.
Culture - CyberSecOp has built a culture of people passionate about Cybersecurity and Professional Services. Uniting around a common goal brings our team together and ensures everyone is working to assist our clients with Cyber Security and compliance. We are a diverse workforce with an open and collaborative culture. Our goal is to be a leading security consulting company by empowering our employees to provide top-quality services measured against best-in-class industry benchmarks.
Customer Success - Customer satisfaction and success continue to be CyberSecOp’s highest priority, measured by retention and the increase in recurring services. Our success is a direct result of the success of our clients.
Our commitment to our mission, staff, clients and partners will continue to fuel our fast growth, creating long-term value for all stakeholders.
What is Your Organization's Cybersecurity Game Plan?
What is Your Organization’s Game Plan for Optimizing Cybersecurity Management?
Like the teams prepping for Sunday's Big Game, cybersecurity and risk management require a playbook to efficiently manage multiple frameworks. Most organizations are going on the offensive with their defensive measures in regards to cybersecurity and risk management. CyberSecOp cybersecurity programs empower your security maturity and culture by utilizing multiple security frameworks to address expanding requirements.
Why is Offensive Defense Important?
Threats like ransomware give attackers the ability to shut down your access to devices, databases and other data streams. While large corporations and government agencies are in attackers’ crosshairs to yield big payouts, small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) are not immune to ransomware risks.
Which Security Framework Can Reduce the Risk of Ransomware?
CyberSecOp provides cyber risk and advisory programs to identify the right security framework for your organization and industry.
How CyberSecOp Assists Our Customers:
To protect against ransomware, CyberSecOp assists clients to implement NIST Cybersecurity Framework and NIST SP 800-207, Zero Trust Architecture to help understand, manage and reduce your cybersecurity risks like phishing and ransomware attacks.
CyberSecOp assist our customers with:
Benefits
Reduce the potential of ransomware encryption
Experienced Security & IT leader
Reduce risk
Build risk assessment program
Third-party risks, privacy compliance and data processing mapping.
Response and mitigation strategies
Security monitoring (SOC & MDR)
GRC platform that incorporates all stages of processing in the risk operational workflow.
Monitor and report on combines and individual frameworks
CyberSecOp cybersecurity experts have been involved in thousands of audit processes at organizations worldwide. Our team has experience with the following framework and regulatory requirements: NIST, PCI, HIPAA, GLBA, SOC, FISMA, GDPR, NYDFS, ISO 27000, SEC, FINRA and others.
Cybersecurity Consulting Career
Cybersecurity consulting is a type of professional service that helps organizations assess their cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities, and provides guidance and recommendations for improving their cybersecurity posture. Cybersecurity consultants typically have a strong background in information technology and cybersecurity, and are skilled in identifying and mitigating potential security threats. They can provide a variety of services, including conducting security assessments, developing and implementing security policies and procedures, providing security training to employees, and assisting with the selection and implementation of cybersecurity technologies and tools.
The goal of cybersecurity consulting is to help organizations protect their systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This can involve identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities, implementing effective security controls, and developing and practicing incident response plans in the event of a security breach. Cybersecurity consultants can work with organizations of all sizes and in a variety of industries, and can provide services on a one-time or ongoing basis, depending on the needs of the organization.
Cybersecurity Consulting Career
A career in cybersecurity consulting can be a rewarding and challenging field, requiring a strong foundation in information technology and cybersecurity, as well as excellent problem-solving, communication, and consulting skills.
To become a cybersecurity consultant, you will typically need to have a bachelor's degree in a related field such as computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity. Some employers may also require a master's degree in a relevant field or industry certifications such as the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
In addition to formal education, practical experience in information technology and cybersecurity is also important for a career in cybersecurity consulting. This may include internships, part-time or full-time work in IT or cybersecurity roles, or participation in cybersecurity-related clubs or organizations.
As a cybersecurity consultant, you may be responsible for working with clients to assess their cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities, and developing and implementing strategies to improve their security posture. This may involve conducting security assessments, developing and implementing security policies and procedures, providing security training to employees, and assisting with the selection and implementation of cybersecurity technologies and tools. You may also be responsible for staying up-to-date on the latest trends and developments in the field, and for maintaining industry certifications as needed.
The demand for cybersecurity professionals, including cybersecurity consultants, is expected to continue to grow in the coming years as organizations of all sizes seek to protect their systems, networks, and data from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of information security analysts, which includes cybersecurity consultants, is projected to grow 31% from 2019 to 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Cyber Security Consultant salary
The salary for a cybersecurity professional, including a cybersecurity consultant, can vary widely depending on a number of factors such as the individual's level of education, experience, skills, certification, and location. According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for information security analysts, which includes cybersecurity consultants, was $99,730 in May 2020.
The BLS also reports that the lowest 10% of information security analysts earned less than $58,480 per year, while the highest 10% earned more than $157,590 per year. Factors that can impact a cybersecurity professional's salary include the industry in which they work, the size of the organization they work for, the location of their job, and the level of responsibility and expertise required for the role.
In addition to salary, many cybersecurity professionals also receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement savings plans, and professional development opportunities. It is worth noting that salaries for cybersecurity professionals can vary significantly depending on the specific role and the specific employer.
Cyber Threats Require New Approach to Design Flaws and Risk
Now that the year is in full swing, and you’re only left with the distant memories, COVID, and cyber security, what are your business cyber objectives for 2022?
Ours goals are to continue helping businesses:
Improving security for everyone, by doubling the amount or organizations we helped last year (100% our client shows no evidence of a data breach)
Offer competitive pricing, to make security an attainable goal for every organization
Reduce cost and increase security by implementing more automation and artificial intelligence
Cyber threats are a real threat to all modern businesses, with the evolution of technology in all sectors. Malicious cyberattacks in 2021 forced shutdown of many business operations at an average downtime of a month. According to multiple reports, the amount of companies who ended paid hackers grew by 300% in 2020, and 200% in 2021. The businesses that were victimized had two options, pay the ransom or go out of business.
Email is the most popular attack vector
Email is still a top attack vector cybercriminal use. A majority of data breaches are caused by attacks on the human layer, but email hacking is much more than phishing.
Top 3 email attacks
Most wire frauds are successful over email communication; the focus trust, in most case the threat actor would be in the middle of a communication between two are more parties. This allows the threat actor to control the conversation, and change wire information.
Threat actor’s setup email rules to keep persistent connections and visibility to gain insight into the organization long after all passwords have been changed.
Threat actors add external emails to distribution groups to keep persistent connect and gain continuous insight into the organization in preparation for their next attack.
Double and Triple Extortion
Cybercriminal groups identified by the FBI responsible for most incidents are known for conducting aggressive “double/triple extortion” ransomware attacks once they have gained access to a network.
In double extortion attacks not only is the victim organization’s data rendered inaccessible until a ransom is paid but the criminals may further monetize the ransomware attack by coupling it with a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack or selling the stolen data onto other criminal groups. In some cases, if the organization is not careful, hackers use email, phone, or text to deceive employees into helping them commit wire fraud.
Providing security is challenging in any industry, whether you’re talking about agriculture, automobiles, furniture, financial services, or educational. It requires special equipment and knowledge around how things can fail in the field, and a disciplined approach to executing tests that reflect real-world conditions as much as possible.
This is where CyberSecOp can help your organization
We are an independent third-party testing, and compliance readiness firm, operating only within the cybersecurity industry. With our comprehensive suite of services and solutions our team can provide continuous testing, security program development, security tabletop exercise, security awareness training to reduce risk and increase critical testing against sensitive systems, using real-world conditions.
Ransomware Protection with Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security Architecture: Why is the Zero Trust Security Model important?
Endpoints represent the most significant attack surface, according to IDC, with over 70% of breaches originating on the endpoint. Organizations have a diverse mix of endpoints connected to their network, whether laptops, mobile endpoints, servers, firewall, wireless hotspots, or IoT devices. Zero-trust architecture works to ensure that users, devices and network traffic are all verified and subjected to least-privilege rules when accessing trusted resources. This way, compromised assets are limited in their scope and an attacker is prevented from moving laterally across the network.
With the rise of remote endpoints and high-profile ransomware attacks, businesses face more cybersecurity threats than ever before. Traditional network security models which assume users and computing devices within the “trusted” network environment are free from compromise and cannot secure organizations. Businesses are also now recognizing that attacks are more sophisticated and that internal networks are no longer more trustworthy than what lies outside the firewall. CyberSecOp and the security community recognized that Zero-trust security is the ultimate protection against ransomware.
Zero Trust Security Optimization
Zero Trust Network (ZTN) concept follows the mantra of never trust, always verify. Through this approach, organizations can reduce their open attack surface and adopt enhanced security capabilities beyond traditional defenses. Zero Trust enables organizations to reduce risk of their cloud and container deployments while also improving governance and compliance. Organizations can gain insight into users and devices while identifying threats and maintaining control across a network.
Traditional – manual configurations and attribute assignment, static security policies, least-function established at provisioning, proprietary and inflexible policy enforcement, manual incident response, and mitigation capability.
Advanced – some cross-solution coordination, centralized visibility, centralized identity control, policy enforcement based on cross-solution inputs and outputs, some incident response to pre-defined mitigations, some least-privilege changes based on posture assessments.
Optimal – fully automated assigning of attributes to assets and resources, dynamic policies based on automated/observed triggers, assets have dynamic least-privilege access (within thresholds), alignment with open standards for cross pillar interoperability, centralized visibility with retention for historical review
10 Ransomware Prevention Best Practices
Below are 10 best practices to help security professionals improve endpoint management:
CyberSecOp Managed Zero Trust security services were built with a new approach that creates zero-trust connections between the users and applications directly to solve this unique challenge. As a scalable, cloud-native platform, it enables digital transformation by securely connecting users,
devices, and applications anywhere, without relying on network-wide access. This platform is delivered by five key architecture attributes, unique to the CyberSecOp Managed Zero Trust Security services that together enable organizations to provide strong security and a great user experience to their employees and customers.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is is an electronic authentication method in which a computer user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication.
Email Security is critical because 74% of organizations in the United States experienced a successful phishing attack. Implementing email security gateway, DMARC, SPF, DKIM, stronger encryption, and MFA can reduce email compromise by over 98%.
CyberSecOp endpoint management solution that supports application isolation and containment technology is a form of zero-trust endpoint security. Instead of detecting or reacting to threats, it enforces controls that block and restrain harmful actions to prevent compromise. Application containment is used to block harmful file and memory actions on other apps on the endpoint. Application isolation is used to prevent other endpoint processes from altering or stealing from an isolated app or resources. This can prevent ransomware from being deployed on devices.
CyberSecOp endpoint management solution support Protective DNS Service (PDNS) refers to a service that provides Domain Name Service (DNS) protection (also known as DNS filtering) by blacklisting dangerous sites and filtering out unwanted content. It can also help to detect & prevent malware that uses DNS such as URL in phishing emails and hiding tunnels to communicate attackers' command and control servers.
CyberSecOp endpoint management solution supports bandwidth throttling so that remote endpoints can be continuously patched and secured rather than having to periodically send IT resources to remote locations. Our solution delivers patch management over the internet without requiring corporate network access. This ensures that internet-facing systems are patched in a proactive, timely manner rather than IT having to wait for these devices to visit the corporate network before they can be scanned and remediated.
CyberSecOp endpoint management reduces administrative overhead of endpoint management solutions to accommodate tight budgets and future growth. Our solutions support many endpoints using a single management system.
Consolidate endpoint management tools. Use a single tool to patch systems across Windows, Mac and variations of Unix operating systems to simplify administration, minimize the number of open network ports, and reduce the number of active agents on endpoints.
Validate that the endpoint management solution provides accurate, real-time endpoint data and reports. End users make changes to endpoints all the time and information that is hours or days old may not reflect a current attack surface.
CyberSecOp endpoint management allows administrators to apply patches that address the highest levels of risk first based on current endpoint status. This gives the biggest impact from remediation efforts.
Make sure the endpoint management solution enforces regulatory and corporate compliance policies on all endpoints constantly to avoid unintended drift and introduction of new vulnerabilities.
To conclude
Ransomware protection needs to go beyond detecting and blocking an initial malware infection at the email perimeter. Malware can enter your organization by other means, and cyber attacks often use the web channel to contact command and control servers and download the encryption keys necessary to complete the cyber attack.
Cybercrime: TOR, Dark Web, Ransomware, and Cryptocurrency
Why cybercrimes love these tools: TOR, Dark Web, Ransomware, and Cryptocurrency
How is TOR, Dark Web, Ransomware, and Cryptocurrency connected when it comes to cybercrime? Cyber criminals use The Onion Router (TOR) in combination with a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to hide their geolocation.
This provides the threat actor with anonymity and privacy, making their connection and identity in some cases untraceable. Cyber criminals use TOR to connect to the dark web where they exchange or purchase illegal goods. This could be hacking tools, drugs, ransomware tools, or even information about your organization. Armed with TOR, VPN, hacking tools, ransomware tools, and organization information they attack organizations to infect their systems with ransomware. Threat actors can also extort a business in the case that they are able to obtain PII or other confidential data on the Dark Web.
At a very high level once the hacker infects an organization system, they encrypt the organization data with ransomware. The encryption renders all data useless. They will also look for other vectors of attack such as deleting shadow copies and other backups they can compromise. The hacker then leaves a ransom note usually demanding payment in cryptocurrency like bitcoin.
I know now you are curious like I was to know more about: TOR, Dark Web, Ransomware, and Cryptocurrency. I have taken the liberty to do just that for you below.
What is TOR?
TOR is short for The Onion Router (thus the logo) and was initially a worldwide network of servers developed with the U.S. Navy that enabled people to browse the internet anonymously. Now, it’s a non-profit organization whose main purpose is the research and development of online privacy tools.
TOR is a free software program that you load onto your computer (like a browser) that hides your IP address every time you send or request data on the Internet. The process is layered with heavy-duty encryption, which means your data is layered with privacy protection. Then there’s the route your data takes as it travels to its destination: TOR will bounce your Internet requests and data through a vast and extensive network of relays (servers) around the world. That data path is never the same because TOR uses up to 5,000 TOR relays to send your data request. Think of it as a huge network of “hidden” servers that will keep your online identity (meaning your IP address) and your location invisible. By using TOR, websites will no longer be able to track the physical location of your IP address or what you have been looking at online…and neither will any interested organizations that may want to monitor someone’s Internet activity—meaning law enforcement or government security agencies. TOR is like a proxy on steroids.
TOR has extreme value because it can work with your website browser, remote log-in applications and even with instant-messaging software. TOR is registered as a nonprofit company, so they run mainly on donations and reliance on the hope that people will become a relay to their network.
What is the Deep and Dark Web and why do you need TOR?
TOR is essential to accessing the dark web. The dark web refers to sites that are not indexed and only accessible via specialized web browsers. Significantly smaller than the tiny surface web, the dark web is considered a part of the deep web. Using our ocean and iceberg visuals, the dark web would be the bottom tip of the submerged iceberg. The dark web, however, is a very concealed portion of the deep web that few will ever interact with or even see. In other words, the deep web covers everything under the surface that's still accessible with the right software, including the dark web.
Breaking down the construction of the dark web reveals a few key layers that make it an anonymous haven:
No webpage indexing by surface web search engines. Google and other popular search tools cannot discover or display results for pages within the dark web. “Virtual traffic tunnels” via a randomized network infrastructure.
Inaccessible by traditional browsers due to its unique registry operator. Also, it's further hidden by various network security measures like firewalls and encryption.
The reputation of the dark web has often been linked to criminal intent or illegal content.
How does ransomware work?
Hackers use TOR to access organization systems to deploy ransomware, so what is ransomware you ask?
Ransomware uses asymmetric encryption. This is cryptography that uses a pair of keys to encrypt and decrypt a file. The public-private pair of keys is uniquely generated by the attacker for the victim, with the private key to decrypt the files stored on the attacker’s server.
The attacker makes the private key available to the victim only after the ransom is paid, though as seen in recent ransomware campaigns, that is not always the case. Without access to the private key, it is nearly impossible to decrypt the files that are being held for ransom. Many variations of ransomware exist. Often ransomware (and other malware) is distributed using email spam campaigns or through targeted attacks. Malware needs an attack vector to establish its presence on an endpoint. After presence is established, malware stays on the system until its task is accomplished.
After a successful exploit, ransomware drops and executes a malicious binary on the infected system. This binary then searches and encrypts valuable files, such as Microsoft Word documents, images, databases, and so on. The ransomware may also exploit system and network vulnerabilities to spread to other systems and possibly across entire organizations. Once files are encrypted, ransomware prompts the user for a ransom to be paid within 24 to 48 hours to decrypt the files, or they will be lost forever. If a data backup is unavailable or those backups were themselves encrypted, the victim is faced with paying the ransom to recover personal files.
What can you do about this?
There are many steps you can take as an individual or an organization to reduce the threat of ransomware exploiting your assets.
· Exercise extreme awareness to spot a phishing or other social engineering attempts
· Harden your devices with Anti Malware, Intrusion Prevention, Firewalls and regular patching
· Backup all important data to an external source in combination with MFA
· Utilize MFA on all applications that are critical
· Perform Vulnerability and Penetration testing to identify weaknesses in your assets
Need help with implementing the above recommendations? Want more information? Reach out to the experts at CyberSecOp and take a proactive step to preventing Ransomware and other types of malware from infecting you.